Safety and immunogenicity of a novel hexavalent group B streptococcus conjugate vaccine in healthy, non-pregnant adults: a phase 1/2, randomised, placebo-controlled, observer-blinded, dose-escalation trial
- PMID: 32891191
- PMCID: PMC9760110
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30478-3
Safety and immunogenicity of a novel hexavalent group B streptococcus conjugate vaccine in healthy, non-pregnant adults: a phase 1/2, randomised, placebo-controlled, observer-blinded, dose-escalation trial
Abstract
Background: Group B streptococcus (GBS) is a major cause of invasive disease in young infants. Infants born to women with sufficient pre-existing anti-GBS capsular IgG antibodies are at reduced risk of GBS disease, making maternal immunisation a potential strategy for prevention. We aimed to assess the safety and immunogenicity of a novel hexavalent (serotypes Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, and V) GBS conjugate vaccine (GBS6).
Methods: This phase 1/2, placebo-controlled, observer-blinded, dose-escalation trial, was done at four clinical research centres in the USA (Kentucky, Georgia, and two sites in Utah). Healthy, non-pregnant adults aged 18-49 years were randomly assigned using an interactive, web-based response technology system. Within each dose group (low, medium, or high), participants in sentinel cohorts were randomly assigned 2:2:1 and expanded cohort participants were randomly assigned 4:4:1 to receive GBS6 with aluminium phosphate (AlPO4), GBS6 without AlPO4, or placebo (saline control). One 0·5 mL dose of either saline placebo or 5 μg capsular polysaccharide per serotype in the low-dose group, 10 μg capsular polysaccharide per serotype in the medium-dose group, or 20 μg capsular polysaccharide per serotype in the high-dose group was administered by intramuscular injection into the deltoid muscle on day 1. The primary outcome was safety up to 6 months after vaccination, including the proportion of sentinel cohort participants with clinical laboratory abnormalities at 1 week, the proportion of all participants reporting solicited local reactions, systemic events, or use of antipyretic or pain medication within 14 days, adverse events up to 1 month, and medically attended or serious adverse events up to 6 months. The secondary outcome was GBS immunogenicity (serotype-specific IgG geometric mean concentrations at 1 month). This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03170609.
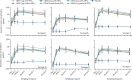
Findings: Between June 5, 2017, and June 25, 2018, 365 participants were randomly assigned and 364 (52 in each dose group) were vaccinated and included in the safety analysis. Unsolicited adverse events were reported by 15 (29%) participants in the 5 μg with AlPO4 group, 13 (25%) in the 5 μg without AlPO4 group, 22 (42%) in the 10 μg with AlPO4 group, 12 (23%) in the 10 μg without AlPO4 group, 25 (48%) in the 20 μg with AlPO4 group, 21 (40%) in the 20 μg without AlPO4 group, and 20 (38%) in the placebo group. The most common unsolicited adverse events were in the system organ class of infections and infestations in any dose or formulation of GBS6 (ranging from six [12%] in the 10 μg without AlPO4 group to 15 [29%] in the 20 μg with AlPO4 group and placebo group). Three participants reported at least one serious adverse event during the study, one each in the 5 μg GBS6 with AlPO4 group (diabetic ketoacidosis, two events; resolved), 10 μg GBS6 with AlPO4 group (died by suicide), and 20 μg GBS6 with AlPO4 group (metrorrhagia; resolved). None of these serious adverse events were considered related to the vaccine. 11 of the 365 participants were excluded from the evaluable immunogenicity population, including one participant who did not receive the vaccine, and ten who at 1 month after vaccination were withdrawn for various reasons. GBS serotype-specific IgG geometric mean concentrations increased by 1 week after vaccination for all GBS6 groups, peaked at 2 weeks, stabilised by 1 month, and declined gradually but remained higher than placebo at 6 months.
Interpretation: GBS6 was well tolerated in healthy adults and elicited robust immune responses for all dose levels and formulations that persisted 6 months after vaccination. This study supports further evaluation of GBS6 in pregnant women.
Funding: Pfizer.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Group B streptococcus vaccines: one step further.Lancet Infect Dis. 2021 Feb;21(2):158-160. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30451-5. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 32891192 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Active bacterial core surveillance (ABCs) report. Emerging infections program network, group B streptococcus. 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/abcs/reports-findings/survreports/gbs17.html Updated April 5, 2019.
-
- Le Doare K, Heath PT. An overview of global GBS epidemiology. Vaccine. 2013;31(suppl 4):D7–12. - PubMed
-
- Johri AK, Lata H, Yadav P, et al. Epidemiology of group B streptococcus in developing countries. Vaccine. 2013;31(suppl 4):D43–D45. - PubMed
-
- Verani JR, McGee L, Schrag SJ. Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease—revised guidelines from CDC, 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010;59:1–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

