Membrane-tethering of cytochrome c accelerates regulated cell death in yeast
- PMID: 32892209
- PMCID: PMC7474732
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02920-0
Membrane-tethering of cytochrome c accelerates regulated cell death in yeast
Abstract
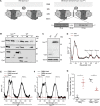
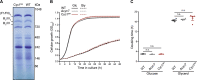
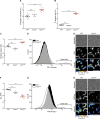
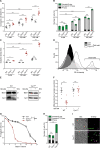
Intrinsic apoptosis as a modality of regulated cell death is intimately linked to permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane and subsequent release of the protein cytochrome c into the cytosol, where it can participate in caspase activation via apoptosome formation. Interestingly, cytochrome c release is an ancient feature of regulated cell death even in unicellular eukaryotes that do not contain an apoptosome. Therefore, it was speculated that cytochrome c release might have an additional, more fundamental role for cell death signalling, because its absence from mitochondria disrupts oxidative phosphorylation. Here, we permanently anchored cytochrome c with a transmembrane segment to the inner mitochondrial membrane of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, thereby inhibiting its release from mitochondria during regulated cell death. This cytochrome c retains respiratory growth and correct assembly of mitochondrial respiratory chain supercomplexes. However, membrane anchoring leads to a sensitisation to acetic acid-induced cell death and increased oxidative stress, a compensatory elevation of cellular oxygen-consumption in aged cells and a decreased chronological lifespan. We therefore conclude that loss of cytochrome c from mitochondria during regulated cell death and the subsequent disruption of oxidative phosphorylation is not required for efficient execution of cell death in yeast, and that mobility of cytochrome c within the mitochondrial intermembrane space confers a fitness advantage that overcomes a potential role in regulated cell death signalling in the absence of an apoptosome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death.Apoptosis. 2007 May;12(5):913-22. doi: 10.1007/s10495-007-0756-2. Apoptosis. 2007. PMID: 17453160 Review.
-
Cardiolipin is not required for Bax-mediated cytochrome c release from yeast mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 9;279(2):1100-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305020200. Epub 2003 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14551208
-
The mitochondrial TOM complex is required for tBid/Bax-induced cytochrome c release.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 21;282(38):27633-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703155200. Epub 2007 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17635912
-
Release of mitochondrial cytochrome C in both apoptosis and necrosis induced by beta-lapachone in human carcinoma cells.Mol Med. 1999 Apr;5(4):232-9. Mol Med. 1999. PMID: 10448645 Free PMC article.
-
Bioenergetics and cell death.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jul;1201:50-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05633.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20649539 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Biochemical Pesticide-Synthesis of Neofuranocoumarin and Inhibition the Proliferation of Spodoptera frugiperda Cells through Activating the Mitochondrial Pathway.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;14(10):677. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100677. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287946 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Yeast Differentiation: From Cell-to-Cell Heterogeneity to Replicative Aging and Regulated Cell Death.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 4;9:823447. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.823447. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35059403 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Quitting Your Day Job in Response to Stress: Cell Survival and Cell Death Require Secondary Cytoplasmic Roles of Cyclin C and Med13.Cells. 2025 Apr 25;14(9):636. doi: 10.3390/cells14090636. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40358161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Proteomics Analysis Reveals Unique Early Signaling Response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to Oxidants with Different Mechanism of Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 26;22(1):167. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010167. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375274 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of direct electron transfer in the robust cytochrome-functionalised graphene nanosystem.RSC Adv. 2021 May 25;11(31):18860-18869. doi: 10.1039/d1ra02419a. eCollection 2021 May 24. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35478629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ott M, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S. Role of cardiolipin in cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:1243–1247. - PubMed
-
- Burke PV, Raitt DC, Allen LA, Kellogg EA, Poyton RO. Effects of oxygen concentration on the expression of cytochrome c and cytochrome c oxidase genes in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:14705–14712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

