Survival and predictors of deaths of patients hospitalised due to COVID-19 from a retrospective and multicentre cohort study in Brazil
- PMID: 32892789
- PMCID: PMC7487752
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268820002034
Survival and predictors of deaths of patients hospitalised due to COVID-19 from a retrospective and multicentre cohort study in Brazil
Abstract
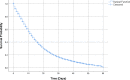
This study aimed to analyse the survival of patients admitted to Brazilian hospitals due to the COVID-19 and estimate prognostic factors. This is a retrospective, multicentre cohort study, based on data from 46 285 hospitalisations for COVID-19 in Brazil. Survival functions were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier's method. The log-rank test compared the survival functions for each variable and from that, hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated, and the proportional hazard model was used in Cox multiple regression. The smallest survival curves were the ones for patients at the age of 68 years or more, black/mixed race, illiterate, living in the countryside, dyspnoea, respiratory distress, influenza-like outbreak, O2 saturation <95%, X-ray change, length of stay in the intensive care unit (ICU), invasive ventilatory support, previous heart disease, pneumopathy, diabetes, Down's syndrome, neurological disease and kidney disease. Better survival was observed in the influenza-like outbreak and in an asthmatic patient. The multiple model for increased risk of death when they were admitted to the ICU HR 1.28, diabetes HR 1.17, neurological disease HR 1.34, kidney disease HR 1.11, heart disease HR 1.14, black or mixed race of HR 1.50, asthma HR 0.71 and pneumopathy HR 1.12. This reinforces the importance of socio-demographic and clinical factors as a prognosis for death.
Keywords: Coronavirus infections; SARS virus; hospitalisations; risk factors; survival analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Meo SA et al. (2020) Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: prevalence, biological and clinical characteristics comparison with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 24, 2012–2019. - PubMed
-
- WHO (2020) Coronavirus disease. World Health Organization, 2019: 2633.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous