Bevacizumab plus cisplatin/pemetrexed then bevacizumab alone for unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma: A Japanese safety study
- PMID: 32893992
- PMCID: PMC8246920
- DOI: 10.1111/ajco.13455
Bevacizumab plus cisplatin/pemetrexed then bevacizumab alone for unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma: A Japanese safety study
Abstract
Aims: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive malignancy with poor prognosis and limited treatment options. Cisplatin plus pemetrexed is the only approved first-line treatment for patients with unresectable MPM. Recently, promising outcomes were observed with first-line bevacizumab combined with cisplatin/pemetrexed, leading to the recommendation of this regimen as a first-line treatment option for patients with MPM. Bevacizumab plus cisplatin/pemetrexed has been shown to be safe and effective in non-small cell lung cancer, however, there are no efficacy or safety data in Japanese patients with MPM treated with this regimen. We conducted a multicenter study to evaluate tolerability and safety for Japanese patients with chemotherapy-naïve, unresectable MPM.
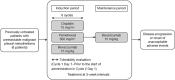
Methods: Eligible patients (n = 7) received bevacizumab plus cisplatin/pemetrexed (up to six cycles), then single-agent bevacizumab until disease progression or onset of unacceptable adverse events (AEs), according to the 3+3 design analogy.
Results: One patient (14.3%) reported an AE (gastric ulcer) meeting tolerability criteria. All patients experienced gastrointestinal disorders, including nausea (grade 1/2 only, n = 6, 85.7%) and constipation (grade 1/2 only, n = 5, 71.4%). Five patients (71.4%) had grade 3 hypertension. Two patients discontinued treatment due to gastric ulcer (n = 1) and proteinuria (n = 1). At data cut-off, four patients had stable disease, two had partial response and one had non-complete response/non-progressive disease due to the absence of target lesions.
Conclusions: Bevacizumab plus cisplatin/pemetrexed then bevacizumab was well tolerated in Japanese patients with MPM.
Keywords: bevacizumab; cisplatin; malignant pleural mesothelioma; pemetrexed; safety.
© 2020 The Authors. Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Takashi Nakano has received honoraria from MSD, Olympus Corporation, ISHIHARA Sangyo, KYORIN Pharmaceutical, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim and ONO Pharmaceutical; acted in a consulting or advisory role for Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim; and reports personal fees from Cancer and Chemotherapy Publishers, Ishiyaku Publishers, IGAKU‐SHOIN, Elsevier Japan K.K., Asakura Publishing, Ministry of the Environment Japan and Amagasaki City, outside the submitted work. Kozo Kuribayashi has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Astellas Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, KYORIN Pharmaceutical, Meiji‐Seika‐Pharma, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical and Taiho Pharmaceutical. Masashi Kondo has received honoraria from Eli Lilly, MSD, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Taiho Pharmaceutical and Kyowa Hakko Kirin. Masahiro Morise has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Serono and Novartis. Yuji Tada has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical. Katsuya Hirano reports personal fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Ono Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Taiho Pharmaceutical and Novartis, outside the submitted work. Morihiko Hayashi and Misa Tanaka are employees of Chugai Pharmaceutical, and Misa Tanaka owns stock in Chugai Pharmaceutical. Masataka Hirabayashi has received honoraria from AstraZeneca K.K., Ono Pharmaceutical, KYORIN Pharmaceutical, Taiho Pharmaceutical, MSD, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet. 2016 Apr 2;387(10026):1405-1414. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01238-6. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 26719230 Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase II Trial of First-Line Combination Chemotherapy With Cisplatin, Pemetrexed, and Nivolumab for Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Study Protocol.Clin Lung Cancer. 2018 Sep;19(5):e705-e707. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 9. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29853412 Clinical Trial.
-
Tumour Treating Fields in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin or carboplatin as first-line treatment for unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (STELLAR): a multicentre, single-arm phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Dec;20(12):1702-1709. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30532-7. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31628016 Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: new agents in clinical trials raise hope of relevant improvements.Curr Opin Oncol. 2014 Mar;26(2):171-81. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000053. Curr Opin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24441503 Review.
-
Malignant pleural mesothelioma: an update on diagnosis and treatment options.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016 Jun;10(3):275-88. doi: 10.1177/1753465816628800. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016. PMID: 26873306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Successful Response to First-Line Carboplatin, Pemetrexed, and Bevacizumab for Peritoneal Mesothelioma: Two Case Reports.Case Rep Oncol. 2025 Jan 30;18(1):278-285. doi: 10.1159/000543889. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40881971
-
Three distinct mechanisms underlying human γδ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity against malignant pleural mesothelioma.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 17;14:1058838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1058838. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006249 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan . Vital statistics in Japan. 2017. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/jinkou/tokusyu/chuuhisyu17/dl/ch... (in Japanese). Accessed June 14, 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

