COVID-19 related reduction in pediatric emergency healthcare utilization - a concerning trend
- PMID: 32894080
- PMCID: PMC7475725
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-020-02303-6
COVID-19 related reduction in pediatric emergency healthcare utilization - a concerning trend
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted healthcare systems worldwide. In addition to the direct impact of the virus on patient morbidity and mortality, the effect of lockdown strategies on health and healthcare utilization have become apparent. Little is known on the effect of the pandemic on pediatric and adolescent medicine. We examined the impact of the pandemic on pediatric emergency healthcare utilization.
Methods: We conducted a monocentric, retrospective analysis of n = 5,424 pediatric emergency department visits between January 1st and April 19th of 2019 and 2020, and compared healthcare utilization during the pandemic in 2020 to the same period in 2019.
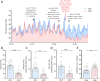
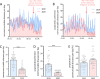
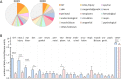
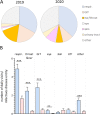
Results: In the four weeks after lockdown in Germany began, we observed a massive drop of 63.8% in pediatric emergency healthcare utilization (mean daily visits 26.8 ± SEM 1.5 in 2019 vs. 9.7 ± SEM 1 in 2020, p < 0.005). This drop in cases occurred for both communicable and non-communicable diseases. A larger proportion of patients under one year old (daily mean of 16.6% ±SEM 1.4 in 2019 vs. 23.1% ±SEM 1.7 in 2020, p < 0.01) and of cases requiring hospitalisation (mean of 13.9% ±SEM 1.6 in 2019 vs. 26.6% ±SEM 3.3 in 2020, p < 0.001) occurred during the pandemic. During the analysed time periods, few intensive care admissions and no fatalities occurred.
Conclusions: Our data illustrate a significant decrease in pediatric emergency department visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Public outreach is needed to encourage parents and guardians to seek medical attention for pediatric emergencies in spite of the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; children; emergency care; emergency department; healthcare utilization; pandemic; pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to report.
Figures

References
-
- Zangrillo A, Beretta L, Silvani P, Colombo S, Scandroglio AM, Dell’Acqua A, Fominskiy E, Landoni G, Monti G, Azzolini ML, et al. Fast reshaping of intensive care unit facilities in a large metropolitan hospital in Milan, Italy: facing the COVID-19 pandemic emergency. Crit Care Resusc. 2020;22(2):91. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

