C-Reactive Protein/Albumin and Neutrophil/Albumin Ratios as Novel Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Schizophrenia
- PMID: 32894927
- PMCID: PMC7538240
- DOI: 10.30773/pi.2020.0185
C-Reactive Protein/Albumin and Neutrophil/Albumin Ratios as Novel Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Schizophrenia
Abstract
Objective: Peripheral biomarker studies in schizophrenia are insufficient to correspond to whether inflammatory markers are trait- or state-related. The main objective of this study was to compare novel biomarkers C-reactive protein/albumin ratio (CAR), neutrophil/albumin ratio (NAR), and complete blood count-derived inflammatory markers; neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR), monocyte/lymphocyte ratio (MLR), red-cell distribution width (RDW), and mean platelet volume (MPV) between patients with acutely exacerbated and remitted schizophrenia and healthy controls.
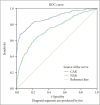
Methods: Anonymous data of a total of 618 patients with schizophrenia (179 in remission, 439 with acute exacerbation) and 445 psychiatrically and medically healthy subjects admitted to outpatient units were included. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD post-hoc test, Pearson's correlation test, receiver operating characteristic analysis, and binomial logistic regression analysis were performed.
Results: CAR, NAR, NLR, PLR, MLR, RDW, MPV values were found higher in patients with schizophrenia than in healthy subjects. Except for NAR (p=0.007), none of the markers differed between acute exacerbation and remission. As a cut-off value of CAR, 0.388 differentiated patients with schizophrenia from controls (sensitivity 81%, specificity 81%). CAR, NAR, and MPV significantly predicted the diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Conclusion: CAR and NAR are reliable biomarkers of inflammation and a combination of inflammatory markers including CAR and NAR could be used to reflect the increased inflammatory status in schizophrenia, regardless of relapse or remission.
Keywords: C-reactive protein-albumin ratio; Inflammation; Relapse; Remission; Schizophrenia; Trait markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Strous RD, Shoenfeld Y. Schizophrenia, autoimmunity and immune system dysregulation: A comprehensive model updated and revisited. J Autoimmun. 2006;27:71–80. - PubMed
-
- Potvin S, Stip E, Sepehry AA, Gendron A, Bah R, Kouassi E. Inflammatory cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: a systematic quantitative review. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:801–808. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

