Occurrence, fates and potential treatment approaches for removal of viruses from wastewater: A review with emphasis on SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32895629
- PMCID: PMC7467108
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104429
Occurrence, fates and potential treatment approaches for removal of viruses from wastewater: A review with emphasis on SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
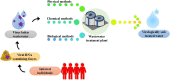
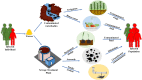
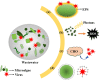
The world is combating the emergence of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by novel coronavirus; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Further, due to the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in sewage and stool samples, its transmission through water routes cannot be neglected. Thus, the efficient treatment of wastewater is a matter of utmost importance. The conventional wastewater treatment processes demonstrate a wide variability in absolute removal of viruses from wastewater, thereby posing a severe threat to human health and environment. The fate of SARS-CoV-2 in the wastewater treatment plants and its removal during various treatment stages remains unexplored and demands immediate attention; particularly, where treated effluent is utilised as reclaimed water. Consequently, understanding the prevalence of pathogenic viruses in untreated/treated waters and their removal techniques has become the topical issue of the scientific community. The key objective of the present study is to provide an insight into the distribution of viruses in wastewater, as well as the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2, and its possible transmission by the faecal-oral route. The review also gives a detailed account of the major waterborne and non-waterborne viruses, and environmental factors governing the survival of viruses. Furthermore, a comprehensive description of the potential methods (physical, chemical, and biological) for removal of viruses from wastewater has been presented. The present study also intends to analyse the research trends in microalgae-mediated virus removal and, inactivation. The review also addresses the UN SDG 'Clean Water and Sanitation' as it is aimed at providing pathogenically safe water for recycling purposes.
Keywords: ASP, Activated Sludge Process; COVID-19; COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019; DUV-LED, Deep Ultraviolet Light-Emitting Diode; E.coli, Escherichia coli; EPS, Exopolysaccharide; LRV, Log Reduction Value; MBR, Membrane Bioreactor; MERS-CoV, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus; MLSS, Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids; Microalgaee; PMR, Photocatalytic Membrane Reactor; Phycoremediationn; RH, Relative Humidity; SARS-CoV, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; SBBGR, Sequencing Batch Biofilter Granular Reactor; SEM, Scanning Electron Microscopy; SSF, Slow Sand Filtration; UASB, Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket; UN SDG, United Nations Sustainable Development Goal; UV, Ultraviolet; WHO, World Health Organisation; WWTP, Wastewater Treatment Plant; Waterbornee; dsDNA, Double stranded Deoxyribonucleic Acid; dsRNA, Double stranded Ribonucleic acid; ssRNA, Single stranded Ribonucleic Acid.
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 in environmental perspective: Occurrence, persistence, surveillance, inactivation and challenges.Chem Eng J. 2021 Feb 1;405:126893. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126893. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Chem Eng J. 2021. PMID: 32901196 Free PMC article.
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor--a review.Indian J Environ Health. 2001 Apr;43(2):1-82. Indian J Environ Health. 2001. PMID: 12397675 Review.
-
Reduction and liquid-solid partitioning of SARS-CoV-2 and adenovirus throughout the different stages of a pilot-scale wastewater treatment plant.Water Res. 2022 Apr 1;212:118069. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118069. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Water Res. 2022. PMID: 35077942 Free PMC article.
-
Removal performance of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater treatment by membrane bioreactor, anaerobic-anoxic-oxic, and conventional activated sludge processes.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Dec 10;851(Pt 2):158310. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158310. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 36030862 Free PMC article.
-
A review on detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater in light of the current knowledge of treatment process for removal of viral fragments.J Environ Manage. 2021 Dec 1;299:113563. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113563. Epub 2021 Aug 19. J Environ Manage. 2021. PMID: 34488114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Survey of Home-Use UV Disinfection Products†.Photochem Photobiol. 2021 May;97(3):560-565. doi: 10.1111/php.13423. Epub 2021 May 4. Photochem Photobiol. 2021. PMID: 33779994 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Burden in Wastewater and its Elimination Using Disinfection.Microbiol Insights. 2023 Sep 22;16:11786361231201598. doi: 10.1177/11786361231201598. eCollection 2023. Microbiol Insights. 2023. PMID: 37745090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elimination of SARS-CoV-2 along wastewater and sludge treatment processes.Water Res. 2021 Sep 1;202:117435. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117435. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Water Res. 2021. PMID: 34330027 Free PMC article.
-
Field grand challenge with emerging superbugs and the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) on plastics and in water.J Environ Chem Eng. 2021 Feb;9(1):104721. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104721. Epub 2020 Nov 5. J Environ Chem Eng. 2021. PMID: 33173752 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the potential of conventional and advanced membrane technology in the removal of pathogens from wastewater.Sep Purif Technol. 2022 Apr 1;286:120454. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120454. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Sep Purif Technol. 2022. PMID: 35035270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xagoraraki I., O’Brien E. Springer, Cham; 2020. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology for Early Detection of Viral Outbreaks; pp. 75–97. - DOI
-
- Tripathi B. 2018. Diarrhoea Took More Lives Than Any Other Water-Borne Disease In India.https://www.indiaspend.com/diarrhoea-took-more-lives-than-any-other-wate... (accessed April 28, 2020)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
