Tocilizumab for severe COVID-19 related illness - A community academic medical center experience
- PMID: 32895645
- PMCID: PMC7467014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytox.2020.100035
Tocilizumab for severe COVID-19 related illness - A community academic medical center experience
Abstract
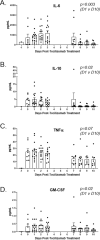
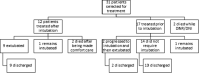
The SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic can result in severe or fatal disease in a subset of infected patients. While the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 disease has yet to be fully elucidated, an overexuberant and harmful immune response to the SARS-CoV-2 virus may be a pivotal aspect of critical illness in this patient population. The inflammatory cytokine, IL-6, has been found to be consistently elevated in severely ill COVID-19 patients, prompting speculation that IL-6 is an important driver of the pathologic process. The inappropriately elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients is similar to cytokine release syndrome (CRS) observed in cell therapy patients. We sought to describe outcomes in a series of severely ill patients with COVID-19 CRS following treatment with anti-IL-6/IL-6-Receptor (anti-IL-6/IL-6-R) therapy, including tocilizumab or siltuximab. At our academic community medical center, we formed a multi-disciplinary committee for selecting severely ill COVID-19 patients for therapy with anti-IL-6 or IL-6-R agents. Key selection criteria included evidence of hyperinflammation, most notably elevated levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and ferritin, and an increasing oxygen requirement. By the data cutoff point, we treated 31 patients with anti-IL-6/IL-6-R agents including 12 who had already been intubated. Overall, 27 (87%) patients are alive and 24 (77%) have been discharged from the hospital. Clinical responses to anti-IL-6/IL-6-R therapy were accompanied by significant decreases in temperature, oxygen requirement, CRP, IL-6, and IL-10 levels. Based on these data, we believe anti-IL-6/IL-6-R therapy can be effective in managing early CRS related to COVID-19 disease. Further study of anti-IL-6/IL-6-R therapy alone and in combination with other classes of therapeutics is warranted and trials are underway.
Keywords: (ALC), Absolute Lymphocyte Count; (ARDS), Acute respiratory distress syndrome; (BMI), Body mass index; (CRP), C-reactive protein; (CRS), Cytokine release syndrome; (DNR/DNI), Do not resuscitate/do not intubate; (ECMO), Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; (ESR), Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; (IRB), Institutional review board; (LDH), Lactate dehydrogenase; (NIV), Noninvasive ventilation; (PaO2/FiO2), Arterial oxygen partial pressure/fraction of inspired oxygen; (RT-PCR), Reverse-transcriptase polymerase-chain-reaction; (RWMC), Roger Williams Medical Center; (SITC), Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer; (SpO2), Peripheral capillary oxygen saturation; (anti-IL-6/IL-6-R), Anti-IL-6/IL-6-Receptor; C-reactive protein; IL-6; Infectious disease; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
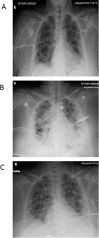
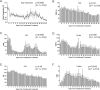
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

