Characterization of the Expression of the ATP-Gated P2X7 Receptor Following Status Epilepticus and during Epilepsy Using a P2X7-EGFP Reporter Mouse
- PMID: 32895896
- PMCID: PMC7674533
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-020-00573-9
Characterization of the Expression of the ATP-Gated P2X7 Receptor Following Status Epilepticus and during Epilepsy Using a P2X7-EGFP Reporter Mouse
Abstract
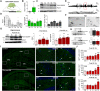
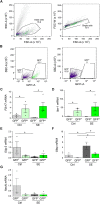
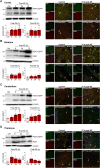
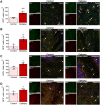
Mounting evidence suggests that the ATP-gated P2X7 receptor contributes to increased hyperexcitability in the brain. While increased expression of P2X7 in the hippocampus and cortex following status epilepticus and during epilepsy has been repeatedly demonstrated, the cell type-specific expression of P2X7 and its expression in extra-hippocampal brain structures remains incompletely explored. In this study, P2X7 expression was visualized by using a transgenic mouse model overexpressing P2X7 fused to the fluorescent protein EGFP. The results showed increased P2X7-EGFP expression after status epilepticus induced by intra-amygdala kainic acid and during epilepsy in different brain regions including the hippocampus, cortex, striatum, thalamus and cerebellum, and this was most evident in microglia and oligodendrocytes. Co-localization of P2X7-EGFP with cell type-specific markers was not detected in neurons or astrocytes. These data suggest that P2X7 activation is a common pathological hallmark across different brain structures, possibly contributing to brain inflammation and neurodegeneration following acute seizures and during epilepsy.
Keywords: Cell type-specific expression; Epilepsy; Green fluorescence protein; P2X7; Purinergic signaling; Status epilepticus.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors claim that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transient P2X7 Receptor Antagonism Produces Lasting Reductions in Spontaneous Seizures and Gliosis in Experimental Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 1;36(22):5920-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4009-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27251615 Free PMC article.
-
Increased neocortical expression of the P2X7 receptor after status epilepticus and anticonvulsant effect of P2X7 receptor antagonist A-438079.Epilepsia. 2013 Sep;54(9):1551-61. doi: 10.1111/epi.12257. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Epilepsia. 2013. PMID: 23808395
-
Deviant reporter expression and P2X4 passenger gene overexpression in the soluble EGFP BAC transgenic P2X7 reporter mouse model.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 16;10(1):19876. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76428-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33199725 Free PMC article.
-
ATPergic signalling during seizures and epilepsy.Neuropharmacology. 2016 May;104:140-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26549853 Review.
-
Beyond Seizure Control: Treating Comorbidities in Epilepsy via Targeting of the P2X7 Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 21;23(4):2380. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216493 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocytes respond to a neurotoxic Aβ fragment with state-dependent Ca2+ alteration and multiphasic transmitter release.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 Mar 16;9(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01146-1. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021. PMID: 33726852 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into pathogenisis and therapies of P2X7R in Parkinson's disease.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025 May 5;11(1):108. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-00980-7. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 40325043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P2X7R antagonism suppresses long-lasting brain hyperexcitability following traumatic brain injury in mice.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 27;15(4):1399-1419. doi: 10.7150/thno.97254. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39886340 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic and Oligodendrocytic P2X7 Receptors Determine Neuronal Functions in the CNS.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Feb 9;14:641570. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.641570. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33642994 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Role of P2X7R in Microglia and Astrocytes.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jul 21;50(4):239. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04502-y. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40690063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Engel T, Alves M, Sheedy C, Henshall DC. ATPergic signalling during seizures and epilepsy. Neuropharmacology. 2016;104:140–153. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Introduction to purinergic signalling in the brain. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1202:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Moshe SL, Perucca E, Ryvlin P. Tomson T. Epilepsy: new advances. Lancet. 2015;385:884–898. - PubMed
-
- Bialer M, White HS. Key factors in the discovery and development of new antiepileptic drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:68–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

