Insights into the unique characteristics of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 revealed by development of a robust sub-genomic DBN3a replicon
- PMID: 32897181
- PMCID: PMC7879556
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001486
Insights into the unique characteristics of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 revealed by development of a robust sub-genomic DBN3a replicon
Abstract
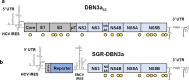
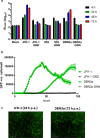
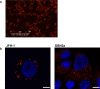
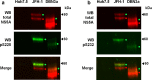
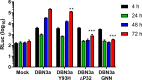
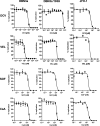
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is an important human pathogen causing 400 000 chronic liver disease-related deaths annually. Until recently, the majority of laboratory-based investigations into the biology of HCV have focused on the genotype 2 isolate, JFH-1, involving replicons and infectious cell culture systems. However, genotype 2 is one of eight major genotypes of HCV and there is great sequence variation among these genotypes (>30 % nucleotide divergence). In this regard, genotype 3 is the second most common genotype and accounts for 30 % of global HCV cases. Further, genotype 3 is associated with both high levels of inherent resistance to direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy, and a more rapid progression to chronic liver diseases. Neither of these two attributes are fully understood, thus robust genotype 3 culture systems to unravel viral replication are required. Here we describe the generation of robust genotype 3 sub-genomic replicons (SGRs) based on the adapted HCV NS3-NS5B replicase from the DBN3a cell culture infectious clone. Such infectious cell culture-adaptive mutations could potentially promote the development of robust SGRs for other HCV strains and genotypes. The novel genotype 3 SGRs have been used both transiently and to establish stable SGR-harbouring cell lines. We show that these resources can be used to investigate aspects of genotype 3 biology, including NS5A function and DAA resistance. They will be useful tools for these studies, circumventing the need to work under the biosafety level 3 (BSL3) containment required in many countries.
Keywords: NS5A; genotype 3; hepatitis C virus; sub-genomic replicon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of full-length cell-culture infectious clone and subgenomic replicon for a genotype 3a isolate of hepatitis C virus.J Gen Virol. 2021 Dec;102(12). doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001704. J Gen Virol. 2021. PMID: 34949310
-
Current status and future development of infectious cell-culture models for the major genotypes of hepatitis C virus: Essential tools in testing of antivirals and emerging vaccine strategies.Antiviral Res. 2018 Oct;158:264-287. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.07.014. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 30059723 Review.
-
Cell Culture Studies of the Efficacy and Barrier to Resistance of Sofosbuvir-Velpatasvir and Glecaprevir-Pibrentasvir against Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes 2a, 2b, and 2c.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Feb 21;64(3):e01888-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01888-19. Print 2020 Feb 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31818814 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of robust HCV genotype 4d, 5a, and 6a replicon systems.Virology. 2018 Jan 15;514:134-141. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Virology. 2018. PMID: 29175627
-
Hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibitors and drug resistance mutations.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Mar 21;20(11):2902-12. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.2902. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24659881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutational analysis reveals a novel role for hepatitis C virus NS5A domain I in cyclophilin-dependent genome replication.J Gen Virol. 2023 Sep;104(9):10.1099/jgv.0.001886. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001886. J Gen Virol. 2023. PMID: 37672027 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus RNA is 5'-capped with flavin adenine dinucleotide.Nature. 2023 Jul;619(7971):811-818. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06301-3. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37407817 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Replicon Systems and Their Biosafety Aspects.Appl Biosaf. 2023 Jun 1;28(2):102-122. doi: 10.1089/apb.2022.0037. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Appl Biosaf. 2023. PMID: 37342518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel substitution in NS5A enhances the resistance of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 to daclatasvir.J Gen Virol. 2021 Jan;102(1):jgv001496. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001496. Epub 2020 Nov 3. J Gen Virol. 2021. PMID: 33141008 Free PMC article.
-
HCV genome-wide analysis for development of efficient culture systems and unravelling of antiviral resistance in genotype 4.Gut. 2022 Mar;71(3):627-642. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323585. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Gut. 2022. PMID: 33833066 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

