Usefulness of argon plasma coagulation for superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasia in patients at high risk or with limited endoscopic resectability
- PMID: 32897227
- PMCID: PMC7480201
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2020.19329
Usefulness of argon plasma coagulation for superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasia in patients at high risk or with limited endoscopic resectability
Abstract
Background/aims: Endoscopic resection is the standard treatment for superficial esophageal squamous-cell neoplasia (SESCN). However, we encounter patients in whom endoscopic resection is difficult to perform. We retrospectively studied the usefulness of argon plasma coagulation (APC) in patients with SESCN.
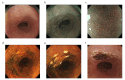
Materials and methods: The study comprised 45 patients with SESCN (81 lesions) who underwent APC in our hospital from March 1999 through August 2016. Clinicopathological characteristics, treatment time, the presence or absence of metastasis and recurrence, adverse events, and outcomes were studied.
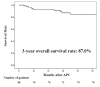
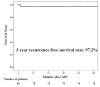
Results: The median follow-up was 40 months. The median age was 70 years. The tumor diameter was 10 mm or longer in 48 lesions and less than 10 mm in 33 lesions. The median treatment time was 22 minutes. The reasons for selecting APC were as follows: technical difficulty caused by the presence of metachronous multiple lesions in the radiation field after chemoradiotherapy or close proximity to the ulcer scar remaining after endoscopic treatment in 49 lesions (60.4%), and the presence of underlying diseases in 26 lesions (32.0%). Adverse events occurred in 2 patients (4.4%) who had hypoxemia due to over-sedation. Two lesions (2.5%) recurred locally but could be locally controlled by additional APC. No patient had metastasis or recurrence or died of esophageal neoplasia. The 3-year overall survival rate was 87.0%, and the 3-year recurrence-free survival rate was 97.2%.
Conclusion: APC can be a useful treatment option for SESCN in patients with a limited life expectancy, poor performance status, or technical difficulty in resection of superficial neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Argon plasma coagulation for superficial esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma in high-risk patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Oct 14;18(38):5412-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5412. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23082058 Free PMC article.
-
Salvage Endoscopic Argon Plasma Coagulation After Chemoradiotherapy for Inoperable Esophageal Cancer.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2017 Oct;27(5):384-390. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000454. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2017. PMID: 28727635
-
Argon plasma coagulation for superficial squamous cell carcinoma in the residual esophagus after esophagectomy.Esophagus. 2020 Oct;17(4):448-455. doi: 10.1007/s10388-020-00733-w. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Esophagus. 2020. PMID: 32211993
-
[Long-term outcomes of endoscopic argon plasma coagulation (APC) therapy for early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013 Jun;35(6):456-8. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24119907 Chinese.
-
[Endoscopic Therapy for Esophageal Cancer].Kyobu Geka. 2016 Jul;69(8):718-23. Kyobu Geka. 2016. PMID: 27440040 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma complicated with varices successfully treated by endoscopic injection sclerotherapy and argon plasma coagulation: A case report.DEN Open. 2024 Feb 28;4(1):e348. doi: 10.1002/deo2.348. eCollection 2024 Apr. DEN Open. 2024. PMID: 38425713 Free PMC article.
-
Repeat endoscopic submucosal dissection close to the initial endoscopic submucosal dissection scar for superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Esophagus. 2024 Oct;21(4):505-513. doi: 10.1007/s10388-024-01074-8. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Esophagus. 2024. PMID: 39068303
-
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Esophageal Cancer: Current and Future.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 27;13(4):892. doi: 10.3390/life13040892. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37109421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Japan Esophageal Society. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of carcinoma of the esophagus. Tokyo: Kanehara Co Ltd; 2017.
-
- Grund KE, Storek D, Farin G. Endoscopic argon plasma coagulation first clinical experiences in flexible endoscopy. Endosc Surg Allied Technol. 1994;2:42–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
