Ifosfamide nephrotoxicity in adult patients
- PMID: 32897279
- PMCID: PMC7467602
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfz183
Ifosfamide nephrotoxicity in adult patients
Abstract
Background: Ifosfamide, a widely prescribed antineoplasic agent, is frequently associated with kidney dysfunction. Its nephrotoxicity is well documented in children, but data are lacking in adult patients.
Methods: The aim of this retrospective study was to describe the clinical, biological and histological characteristics of ifosfamide nephrotoxicity.
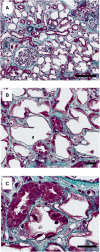
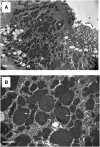
Results: We report 34 patients (median age: 41 years) admitted in six French nephrology departments for kidney failure and/or tubular dysfunction. Fifteen patients (44.1%) received cisplatin as part of their chemotherapy. In 6 patients (17.7%), ifosfamide nephrotoxicity was revealed by a proximal tubular dysfunction (PTD), in 5 patients (14.4%) by an acute kidney injury (AKI), in 6 patients (17.7%) by a chronic kidney disease (CKD) and in 17 patients (49.7%) by an association of PTD and AKI. Fourteen renal biopsies (41.2%) were performed and revealed acute tubular necrosis (85.7%), vacuolation (78.6%) and nuclear atypias (71.4%) of renal epithelial cells, interstitial inflammation (71.4%) and fibrosis (57.1%). Electron microscopy showed mitochondrial enlargement and dysmorphic changes suggestive of mitochondrial toxicity. Ten patients (29.4%) progressed to Stage 5 CKD, six (17.6%) required haemodialysis and six patients died during a median follow-up period of 31 months. Risk factors for Stage 5 CKD were age and cisplatin co-administration.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; chronic kidney injury; ifosfamide; mitochondrial toxicity; nephrotoxicity; proximal tubular dysfunction.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures

References
-
- Basaran M, Bavbek ES, Saglam S. et al. A phase II study of cisplatin, ifosfamide and epirubicin combination chemotherapy in adults with nonmetastatic and extremity osteosarcomas. Oncology 2007; 72: 255–260 - PubMed
-
- Hartmann JT, Gauler T, Metzner B. et al. Phase I/II study of sequential dose-intensified ifosfamide, cisplatin, and etoposide plus paclitaxel as induction chemotherapy for poor prognosis germ cell tumors by the German Testicular Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 5742–5747 - PubMed
-
- Schütt P, Passon J, Ebeling P. et al. Ifosfamide, etoposide, cytarabine, and dexamethasone as salvage treatment followed by high-dose cyclophosphamide, melphalan, and etoposide with autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for relapsed or refractory lymphomas. Eur J Haematol 2006; 78: 93–101 - PubMed
-
- Van Dyk JJ, Falkson HC, Van der Merwe AM. et al. Unexpected toxicity in patients treated with iphosphamide. Cancer Res 1972; 32: 921–924 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

