Biodistribution of degradable polyanhydride particles in Aedes aegypti tissues
- PMID: 32898130
- PMCID: PMC7500644
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008365
Biodistribution of degradable polyanhydride particles in Aedes aegypti tissues
Abstract
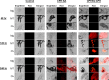
Insecticide resistance poses a significant threat to the control of arthropods that transmit disease agents. Nanoparticle carriers offer exciting opportunities to expand the armamentarium of insecticides available for public health and other pests. Most chemical insecticides are delivered by contact or feeding, and from there must penetrate various biological membranes to reach target organs and kill the pest organism. Nanoparticles have been shown to improve bioactive compound navigation of such barriers in vertebrates, but have not been well-explored in arthropods. In this study, we explored the potential of polyanhydride micro- and nanoparticles (250 nm- 3 μm), labeled with rhodamine B to associate with and/or transit across insect biological barriers, including the cuticle, epithelium, midgut and ovaries, in female Ae. aeygpti mosquitoes. Mosquitoes were exposed using conditions to mimic surface contact with a residual spray or paint, topical exposure to mimic contact with aerosolized insecticide, or per os in a sugar meal. In surface contact experiments, microparticles were sometimes observed in association with the exterior of the insect cuticle. Nanoparticles were more uniformly distributed across exterior tissues and present at higher concentrations. Furthermore, by surface contact, topical exposure, or per os, particles were detected in internal organs. In every experiment, amphiphilic polyanhydride nanoparticles associated with internal tissues to a higher degree than hydrophobic nanoparticles. In vitro, nanoparticles associated with Aedes aegypti Aag2 cells within two hours of exposure, and particles were evident in the cytoplasm. Further studies demonstrated that particle uptake is dependent on caveolae-mediated endocytosis. The propensity of these nanoparticles to cross biological barriers including the cuticle, to localize in target tissue sites of interest, and to reach the cytoplasm of cells, provides great promise for targeted delivery of insecticidal candidates that cannot otherwise reach these cellular and subcellular locations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






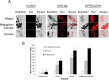


References
-
- Webb JE, Green RA. 1945. On the penetration of insecticides through the insect cuticle. J Exp Biol.22: 8–20. - PubMed
-
- Hurst H. Permeability of insect cuticle. 1940. Nature. 45: 462–463.
-
- Rockstein M. 1973. The Physiology of Insecta. 2nd ed. Elsevier Science Ltd;
-
- Chapman RF. 2012. The Insects: Structure and Function. 5th ed. Cambridge University Press.
-
- Halstead NT, Civitello DJ, Rohr JR. 2015. Comparative toxicities of organophosphate and pyrethroid insecticides to aquatic macroarthropods. Chemosphere. 35: 265–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

