A combination of 7-ketocholesterol, lysosphingomyelin and bile acid-408 to diagnose Niemann-Pick disease type C using LC-MS/MS
- PMID: 32898135
- PMCID: PMC7478639
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238624
A combination of 7-ketocholesterol, lysosphingomyelin and bile acid-408 to diagnose Niemann-Pick disease type C using LC-MS/MS
Abstract
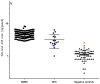
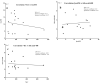
Background: Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations of NPC1 or NPC2, which encode the proteins that are responsible for intracellular cholesterol trafficking. Loss of this function results in the accumulation of cholesterol-related products, such as oxysterols, sphingolipids, and NPC-related bile acids, which were recently used as biochemical biomarkers for the diagnosis of NPC. Bile acid-408 is a new significant compound we found in Japanese NPC patients, and it likely belongs to the category of bile acids. However, the diagnosis of NPC using a single biomarker is not satisfactory for clinical application because of the high instance of false negatives or positives. Therefore, we proposed an application of NPC diagnosis using a combination of 7-ketocholesterol (7-KC), lysosphingomyelin (lysoSM), bile acid-408 and/or glucosylsphingosine (lysoGL-1).
Methods and findings: 7-KC, lysoSM and lysoGL-1 in sera and bile acid-408 in dried blood spots (DBS) were quantified within 17 minutes using tandem mass spectrometry and high-resolution mass spectrometry, respectively. We measured these biomarkers in NPC patients (n = 19), X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) patients (n = 5), patients with other lysosomal diseases (n = 300), newborns (n = 124) and healthy people (n = 74). Our results showed a promising accuracy (97%) for NPC diagnosis using the combination of 7-KC, lysoSM and bile acid-408. However, contrary to our expectations, lysoGL-1 levels did not present at a significantly greater amount in NPC patients than other patients and negative controls.
Conclusions: The combination of 7-KC, lysoSM and bile acid-408 improves the accuracy of NPC diagnosis and is feasible for mass screening due to its simple sample preparation and measurement. Future research should investigate the chemical structure of bile acid-408 to further facilitate its advantage in diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
AnGes Inc. provided support in the form of salaries for authors [C. Wu, J. Igarashi, T. Miyajima]. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products associated with this research to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantitation of plasmatic lysosphingomyelin and lysosphingomyelin-509 for differential screening of Niemann-Pick A/B and C diseases.Anal Biochem. 2017 May 15;525:73-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2017.02.019. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Anal Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28259515
-
Diagnosis of niemann-pick C1 by measurement of bile acid biomarkers in archived newborn dried blood spots.Mol Genet Metab. 2019 Feb;126(2):183-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.08.007. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Mol Genet Metab. 2019. PMID: 30172462 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma lysosphingomyelin demonstrates great potential as a diagnostic biomarker for Niemann-Pick disease type C in a retrospective study.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 5;9(12):e114669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114669. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25479233 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic tests for Niemann-Pick disease type C (NP-C): A critical review.Mol Genet Metab. 2016 Aug;118(4):244-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Mol Genet Metab. 2016. PMID: 27339554 Review.
-
Laboratory diagnosis of the Niemann-Pick type C disease: an inherited neurodegenerative disorder of cholesterol metabolism.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Oct;34(5):1253-1260. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-00445-w. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 31197681 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Neurofilament Light (NfL) in Patients Affected by Niemann-Pick Type C Disease (NPCD).J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 19;10(20):4796. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204796. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34682919 Free PMC article.
-
Oxysterols: From redox bench to industry.Redox Biol. 2022 Feb;49:102220. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102220. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 34968886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Niemann-Pick type C disease as proof-of-concept for intelligent biomarker panel selection in neurometabolic disorders.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2022 Dec;64(12):1539-1546. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15334. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35833379 Free PMC article.
-
Global Proteomics for Identifying the Alteration Pathway of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Using Hepatic Cell Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 27;24(21):15642. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115642. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958627 Free PMC article.
-
Wide-Targeted Semi-Quantitative Analysis of Acidic Glycosphingolipids in Cell Lines and Urine to Develop Potential Screening Biomarkers for Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 7;25(7):4098. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074098. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patterson MC, Vanier MT, Suzuki K, Morris JA, Carstea E, Neufeld EB, et al. Niemann-Pick Disease Type C: A Lipid Trafficking Disorder. In: Valle D, Beaudet AL, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, Antonarakis SE, Ballabio A, Gibson KM, Mitchell G, editors. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

