PI3Kδ inhibition reshapes follicular lymphoma-immune microenvironment cross talk and unleashes the activity of venetoclax
- PMID: 32898249
- PMCID: PMC7479943
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001584
PI3Kδ inhibition reshapes follicular lymphoma-immune microenvironment cross talk and unleashes the activity of venetoclax
Abstract
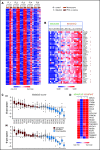
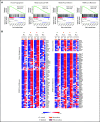
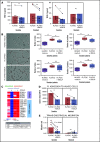
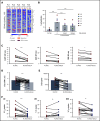
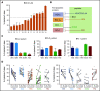
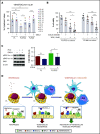
Despite idelalisib approval in relapsed follicular lymphoma (FL), a complete characterization of the immunomodulatory consequences of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase δ (PI3Kδ) inhibition, biomarkers of response, and potential combinatorial therapies in FL remain to be established. Using ex vivo cocultures of FL patient biopsies and follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) to mimic the germinal center (n = 42), we uncovered that PI3Kδ inhibition interferes with FDC-induced genes related to angiogenesis, extracellular matrix formation, and transendothelial migration in a subset of FL samples, defining an 18-gene signature fingerprint of idelalisib sensitivity. A common hallmark of idelalisib found in all FL cases was its interference with the CD40/CD40L pathway and induced proliferation, together with the downregulation of proteins crucial for B-T-cell synapses, leading to an inefficient cross talk between FL cells and the supportive T-follicular helper cells (TFH). Moreover, idelalisib downmodulates the chemokine CCL22, hampering the recruitment of TFH and immunosupressive T-regulatory cells to the FL niche, leading to a less supportive and tolerogenic immune microenvironment. Finally, using BH3 profiling, we uncovered that FL-FDC and FL-macrophage cocultures augment tumor addiction to BCL-XL and MCL-1 or BFL-1, respectively, limiting the cytotoxic activity of the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax. Idelalisib restored FL dependence on BCL-2 and venetoclax activity. In summary, idelalisib exhibits a patient-dependent activity toward angiogenesis and lymphoma dissemination. In all FL cases, idelalisib exerts a general reshaping of the FL immune microenvironment and restores dependence on BCL-2, predisposing FL to cell death, providing a mechanistic rationale for investigating the combination of PI3Kδ inhibitors and venetoclax in clinical trials.
© 2020 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.Y. and S.T. were Gilead Sciences employees and P.P.-G. received research funding from Gilead Sciences. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Huet S, Sujobert P, Salles G. From genetics to the clinic: a translational perspective on follicular lymphoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(4):224-239. - PubMed
-
- Lackraj T, Goswami R, Kridel R. Pathogenesis of follicular lymphoma. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2018;31(1):2-14. - PubMed
-
- Amé-Thomas P, Tarte K. The yin and the yang of follicular lymphoma cell niches: role of microenvironment heterogeneity and plasticity. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;24:23-32. - PubMed
-
- Linley A, Krysov S, Ponzoni M, Johnson PW, Packham G, Stevenson FK. Lectin binding to surface Ig variable regions provides a universal persistent activating signal for follicular lymphoma cells. Blood. 2015;126(16):1902-1910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

