A systematic, label-free method for identifying RNA-associated proteins in vivo provides insights into vertebrate ciliary beating machinery
- PMID: 32898505
- PMCID: PMC7668317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.08.008
A systematic, label-free method for identifying RNA-associated proteins in vivo provides insights into vertebrate ciliary beating machinery
Abstract
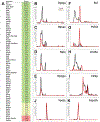
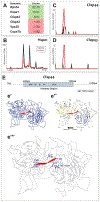
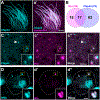
Cell-type specific RNA-associated proteins are essential for development and homeostasis in animals. Despite a massive recent effort to systematically identify RNA-associated proteins, we currently have few comprehensive rosters of cell-type specific RNA-associated proteins in vertebrate tissues. Here, we demonstrate the feasibility of determining the RNA-associated proteome of a defined vertebrate embryonic tissue using DIF-FRAC, a systematic and universal (i.e., label-free) method. Application of DIF-FRAC to cultured tissue explants of Xenopus mucociliary epithelium identified dozens of known RNA-associated proteins as expected, but also several novel RNA-associated proteins, including proteins related to assembly of the mitotic spindle and regulation of ciliary beating. In particular, we show that the inner dynein arm tether Cfap44 is an RNA-associated protein that localizes not only to axonemes, but also to liquid-like organelles in the cytoplasm called DynAPs. This result led us to discover that DynAPs are generally enriched for RNA. Together, these data provide a useful resource for a deeper understanding of mucociliary epithelia and demonstrate that DIF-FRAC will be broadly applicable for systematic identification of RNA-associated proteins from embryonic tissues.
Keywords: Cilia; DIF-FRAC; Proteomics; RNA; Xenopus.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ariizumi T, Takahashi S, Chan T.c., Ito Y, Michiue T, and Asashima M. 2009. Isolation and differentiation of Xenopus animal cap cells. Current protocols in stem cell biology. 9:1D. 5.1–1D. 5.31. - PubMed
-
- Baltz AG, Munschauer M, Schwanhausser B, Vasile A, Murakawa Y, Schueler M, Youngs N, Penfold-Brown D, Drew K, Milek M, Wyler E, Bonneau R, Selbach M, Dieterich C, and Landthaler M. 2012. The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Mol. Cell 46:674–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

