The kinetics of viral load and antibodies to SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32898715
- PMCID: PMC7474805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.043
The kinetics of viral load and antibodies to SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Objectives: The aim was to understand persistence of the virus in body fluids the and immune response of an infected host to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), an agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods: We determined the kinetics of viral load in several body fluids through real time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, serum antibodies of IgA, IgG and IgM by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and neutralizing antibodies by microneutralization assay in 35 COVID-19 cases from two hospitals in Guangdong, China.
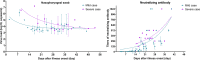
Results: We found higher viral loads and prolonged shedding of virus RNA in severe cases of COVID-19 in nasopharyngeal (1.3 × 106 vs 6.4 × 104, p < 0.05; 7∼8 weeks) and throat (6.9 × 106 vs 2.9 × 105, p < 0.05; 4∼5 weeks), but similar in sputum samples (5.5 × 106 vs 0.9 × 106, p < 0.05; 4∼5 weeks). Viraemia was rarely detected (2.8%, n = 1/35). We detected early seroconversion of IgA and IgG at the first week after illness onset (day 5, 5.7%, n = 2/35). Neutralizing antibodies were produced in the second week, and observed in all 35 included cases after the third week illness onset. The levels of neutralizing antibodies correlated with IgG (rs = 0.85, p < 0.05; kappa = 0.85) and IgA (rs = 0.64, p < 0.05; kappa = 0.61) in severe, but not mild cases (IgG, rs = 0.42, kappa = 0.33; IgA, rs = 0.32, kappa = 0.22). No correlation with IgM in either severe (rs = 0.17, kappa = 0.06) or mild cases (rs = 0.27, kappa = 0.15) was found.
Discussion: We revealed a prolonged shedding of virus RNA in the upper respiratory tract, and evaluated the consistency of production of IgG, IgA, IgM and neutralizing antibodies in COVID-19 cases.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgA; IgG; IgM; Neutralizing antibodies; SARS-CoV-2; Viral load.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Sun J., Su J., Jiao X., Zhou H., Zhang H., Wu D. Community based serosurvey of naïve population indicate no local circulation of Zika virus in an hyper endemic area of China 2016. J Infect. 2019;7:61–74. - PubMed
-
- Li G., Chen X., Xu A. Profile of specific antibodies to the SARS-associated coronavirus. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:508–509. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

