First-line pemetrexed and carboplatin plus anlotinib for epidermal growth factor receptor wild-type and anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastasis: A case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 32899099
- PMCID: PMC7478551
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022128
First-line pemetrexed and carboplatin plus anlotinib for epidermal growth factor receptor wild-type and anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastasis: A case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Rationale: Brain metastasis (BM) is a serious complication in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Pemetrexed is one of the preferred agents in nonsquamous NSCLC with BM; however, the traditional chemotherapy demonstrated limited efficacy partly due to drug resistance and the blood-brain barrier.
Patient concerns: A 52-year-old male non-smoker was admitted for irritating cough, chest distress, and back pain.
Diagnoses: Epidermal growth factor receptor wild-type, anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative primary lung adenocarcinoma with an asymptomatic solitary BM (cTxNxM1b, IVA).
Interventions: Pemetrexed (500 mg/m of body surface area) and carboplatin (area under the curve of 5) were firstly administered every 3 weeks for 3 cycles, followed by pemetrexed/carboplatin plus anlotinib (12 mg daily; 2 weeks on and 1 week off) for another 3 cycles. Then maintenance anlotinib monotherapy was continued for a year, without unacceptable adverse events.
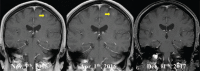
Outcomes: The BM was slightly enlarged after 3 cycles of pemetrexed/carboplatin; however, a complete remission was achieved after the combination therapy. His intracranial progression-free survival was more than 2 years.
Lessons: Pemetrexed/carboplatin plus anlotinib could be considered for the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor wild-type, anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative lung adenocarcinoma with BM. Further well-designed trials are warranted to verify this occasional finding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

