PET Radiotracers for CNS-Adrenergic Receptors: Developments and Perspectives
- PMID: 32899124
- PMCID: PMC7504810
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25174017
PET Radiotracers for CNS-Adrenergic Receptors: Developments and Perspectives
Abstract
Epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) play diverse roles in our body's physiology. In addition to their role in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), E/NE systems including their receptors are critical to the central nervous system (CNS) and to mental health. Various antipsychotics, antidepressants, and psychostimulants exert their influence partially through different subtypes of adrenergic receptors (ARs). Despite the potential of pharmacological applications and long history of research related to E/NE systems, research efforts to identify the roles of ARs in the human brain taking advantage of imaging have been limited by the lack of subtype specific ligands for ARs and brain penetrability issues. This review provides an overview of the development of positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracers for in vivo imaging of AR system in the brain.
Keywords: adrenergic receptor; positron emission tomography; radiotracer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

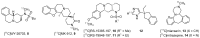
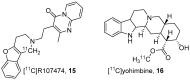

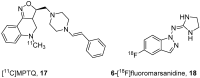
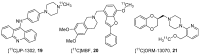
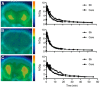
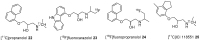
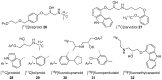
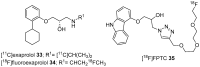
References
-
- Scott J.A. Positron Emission Tomography: Basic Science and Clinical Practice. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004;182:418. doi: 10.2214/ajr.182.2.1820418. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

