Rocuronium Has a Suppressive Effect on Platelet Function via the P2Y12 Receptor Pathway In Vitro That Is Not Reversed by Sugammadex
- PMID: 32899133
- PMCID: PMC7504164
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21176399
Rocuronium Has a Suppressive Effect on Platelet Function via the P2Y12 Receptor Pathway In Vitro That Is Not Reversed by Sugammadex
Abstract
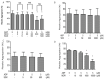
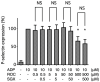
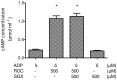
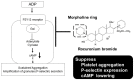
Rocuronium is an aminosteroid nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker that is widely used for anesthesia and intensive care. In this study, we investigated the effect of rocuronium on human platelet functions in vitro. The effects of rocuronium on platelet aggregation, P-selectin expression, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels in platelets were measured using an aggregometer, an enzyme immunoassay, and flow cytometry, respectively. Rocuronium inhibited ADP-induced platelet aggregation, P-selectin expression and suppression of cAMP production. These effects were not antagonized by equimolar sugammadex, a synthetic γ-cyclodextrin derivative that antagonizes rocuronium-induced muscle relaxation by encapsulating the rocuronium molecule. Morpholine, which constitutes a part of the rocuronium molecule but is not encapsulated by sugammadex, inhibited ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Vecuronium, which has a molecular structure similar to that of rocuronium but does not possess a morpholine ring, had no significant effect on ADP-induced platelet aggregation. These results indicate that rocuronium has a suppressive effect on platelet functions in vitro that is not reversed by sugammadex and suggest that this effect is mediated by blockade of the P2Y12 receptor signaling pathway via the morpholine ring of rocuronium.
Keywords: P2Y12 receptor; cyclodextrin; morpholine; platelet; rocuronium; sugammadex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hirakata H., Hatano Y., Ushikubi F., Mori K., Narumiya S., Nakamura K. The Effect of Inhaled Anesthetics on the Platelet Aggregation and the Ligand-Binding Affinity of the Platelet Thromboxane A2 Receptor. Anesth. Analg. 1995;81:114–118. - PubMed
-
- Hirakata H., Ushikubi F., Toda H., Nakamura K., Sai S., Urabe N., Hatano Y., Narumiya S., Mori K. Sevoflurane inhibits human platelet aggregation and thromboxane A 2 formation, possibly by suppression of cyclooxygenase activity. Anesthesiology. 1996;85:1447–1453. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199612000-00027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa T., Hirakata H., Sato M., Nakamura K., Hatano Y., Nakamura T., Fukuda K. Ketamine suppresses platelet aggregation possibly by suppressed inositol triphosphate formation and subsequent suppression of cytosolic calcium increase. Anesthesiology. 2002;96:1147–1152. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200205000-00018. - DOI - PubMed

