Ubiquinone Supplementation with 300 mg on Glycemic Control and Antioxidant Status in Athletes: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 32899227
- PMCID: PMC7555239
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9090823
Ubiquinone Supplementation with 300 mg on Glycemic Control and Antioxidant Status in Athletes: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
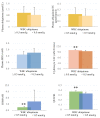
The aim of this study is to investigate the glycemic profile, oxidative stress, and antioxidant capacity in athletes after 12 weeks of ubiquinone supplementation. It was a double-blinded, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled study. Thirty-one well-trained college athletes were randomly assigned to ubiquinone (300 mg/d, n = 17) or placebo group (n = 14). The glycemic profile [fasting glucose, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), homeostatic model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI)], plasma and erythrocyte malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), and ubiquinone status were measured. After supplementation, the plasma ubiquinone concentration was significantly increased (p < 0.05) and the level of erythrocyte MDA was significantly lower in the ubiquinone group than in the placebo group (p < 0.01). There was a significant correlation between white blood cell (WBC) ubiquinone and glycemic parameters [HbA1c, r = -0.46, p < 0.05; HOMA-IR, r = -0.67, p < 0.01; QUICKI, r = 0.67, p < 0.01]. In addition, athletes with higher WBC ubiquinone level (≥0.5 nmol/g) showed higher erythrocyte TAC and QUICKI and lower HOMA-IR. In conclusion, we demonstrated that athletes may show a better antioxidant capacity with higher ubiquinone status after 12 weeks of supplementation, which may further improve glycemic control.
Keywords: antioxidant; athletes; glycaemia; sport nutrition; ubiquinone supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coenzyme Q10 status, glucose parameters, and antioxidative capacity in college athletes.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020 Jan 10;17(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-0334-3. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31924223 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Metabolic Response to Selenium Supplementation in Pregnant Women at Risk for Intrauterine Growth Restriction: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017 Jul;178(1):14-21. doi: 10.1007/s12011-016-0911-0. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017. PMID: 27928721 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of coenzyme Q10 administration on glucose homeostasis parameters, lipid profiles, biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with metabolic syndrome.Eur J Nutr. 2016 Dec;55(8):2357-2364. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-1042-7. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26385228 Clinical Trial.
-
Grape Seed Extract Supplementation and the Effects on the Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Profiles in Female Volleyball Players: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2016 Jul 17;18(9):e31314. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.31314. eCollection 2016 Sep. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2016. PMID: 28144458 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of vitamin D supplementation on indices of glycemic control in Iranian diabetics: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2019 Feb;34:294-304. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2018.12.009. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 30712741
Cited by
-
One-Year Changes in Urinary Microbial Phenolic Metabolites and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes-A Case-Control Study.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 8;11(8):1540. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081540. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009259 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation and Its Impact on Exercise and Sport Performance in Humans: A Recovery or a Performance-Enhancing Molecule?Nutrients. 2022 Apr 26;14(9):1811. doi: 10.3390/nu14091811. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35565783 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Therapeutic Roles of Plant-Derived Antioxidants in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Considerations for Special Populations.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;14(6):725. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060725. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Adults: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 13;11(7):1360. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071360. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation in Athletes: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 15;15(18):3990. doi: 10.3390/nu15183990. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

