Differential Expression of Circulating Plasma miRNA-370 and miRNA-10a from Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
- PMID: 32899377
- PMCID: PMC7565099
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9092855
Differential Expression of Circulating Plasma miRNA-370 and miRNA-10a from Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Abstract
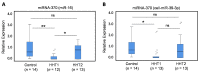
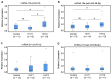
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is an autosomal dominant, vascular disorder that presents with telangiectases and arteriovenous malformations. HHT is a genetically heterogeneous disorder, involving mutations in endoglin (ENG; HHT1) and activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ACVRL1/ALK1; HHT2) genes that account for over 85% of all HHT patients. The current diagnosis of HHT patients remains at the clinical level, but many suspected patients do not have a clear HHT diagnosis or do not show pathogenic mutations in HHT genes. This situation has prompted the search for biomarkers to help in the early diagnosis of the disease. We have analyzed the plasma levels in HHT patients of selected micro-RNAs (miRNAs), small single-stranded RNAs that regulate gene expression at the transcriptional level by interacting with specific RNA targets. A total of 16 HHT1 and 17 HHT2 plasma samples from clinically confirmed patients and 16 controls were analyzed in this study. Total RNA was purified from plasma, and three selected miRNAs (miRNA-10a, miRNA-214, and miRNA-370), related to the pathobiology of cardiovascular diseases and potentially targeting ENG or ALK1, were measured by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Compared with controls, levels of miRNA-370, whose putative target is ENG, were significantly downregulated in HHT1, but not in HHT2, whereas the levels of miRNA-10a, whose putative target is ALK1, were significantly upregulated in HHT2, but not in HHT1. In addition, the levels of miRNA-214, potentially targeting ENG and ALK1, did not change in either HHT1 or HHT2 patients versus control samples. While further studies are warranted, these results suggest that dysregulated plasma levels of miRNA-370 or miRNA-10a could help to identify undiagnosed HHT1 or HHT2 patients, respectively.
Keywords: activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1); angiogenesis; arteriovenous malformations (AVMs); biomarker; bone morphogenetic protein (BMP); endoglin; hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT); microRNA; plasma; telangiectases; transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of endoglin receptor impairs mononuclear cell-migration.Explor Med. 2020;1:136-148. doi: 10.37349/emed.2020.00010. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Explor Med. 2020. PMID: 32954380 Free PMC article.
-
Endoglin and alk1 as therapeutic targets for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Oct;21(10):933-947. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1365839. Epub 2017 Aug 20. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28796572 Review.
-
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in Japanese patients.J Hum Genet. 2014 Jan;59(1):37-41. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2013.113. Epub 2013 Nov 7. J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24196379
-
Anti-angiogenic therapeutic strategies in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Front Genet. 2015 Feb 11;6:35. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00035. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25717337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen therapy for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT): Effects of raloxifene, on Endoglin and ALK1 expression in endothelial cells.Thromb Haemost. 2010 Mar;103(3):525-34. doi: 10.1160/TH09-07-0425. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20135064
Cited by
-
Non-Coding RNAs and Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia.J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 17;9(10):3333. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103333. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33080889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of nuclear medicine in a case of Rendu-Osler-Weber disease with pulmonary involvement.World J Nucl Med. 2021 Sep 22;20(4):389-391. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.wjnm_48_21. eCollection 2021 Oct-Dec. World J Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 35018158 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-132-3p, Downregulated in Myeloid Angiogenic Cells from Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Patients, Is Enriched in the TGFβ and PI3K/AKT Signalling Pathways.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 9;13(4):665. doi: 10.3390/genes13040665. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456471 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of MiRs-139-5p and -454-3p in Endoglin-Knockdown-Induced Angiogenic Dysfunction in HUVECs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 3;24(5):4916. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054916. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902347 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Endoglin and Malignant Phenotype in Human Melanoma Cells: Analysis of hsa-mir-214 and hsa-mir-370 in Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1408:253-272. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26163-3_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37093432
References
-
- Shovlin C.L., Guttmacher A.E., Buscarini E., Faughnan M.E., Hyland R.H., Westermann C.J.J., Kjeldsen A.D., Plauchu H. Diagnostic criteria for Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (Rendu- Osler-Weber Syndrome) Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000;91:66–67. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(20000306)91:1<66::AID-AJMG12>3.0.CO;2-P. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shovlin C.L., Buscarini E., Kjeldsen A.D., Mager H.J., Sabba C., Droege F., Geisthoff U., Ugolini S., Dupuis-Girod S. European Reference Network for Rare Vascular Diseases (VASCERN) Outcome Measures for Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) Orphanet. J. Rare. Dis. 2018;13:136. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0850-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Faughnan M.E., Palda V.A., Garcia-Tsao G., Geisthoff U.W., McDonald J., Proctor D.D., Spears J., Brown D.H., Buscarini E., Chesnutt M.S., et al. International guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J. Med. Genet. 2011;48:73–87. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2009.069013. - DOI - PubMed

