Genetic Hypothesis and Pharmacogenetics Side of Renin-Angiotensin-System in COVID-19
- PMID: 32899439
- PMCID: PMC7563402
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11091044
Genetic Hypothesis and Pharmacogenetics Side of Renin-Angiotensin-System in COVID-19
Abstract
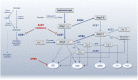
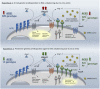
The importance of host genetics and demography in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a crucial aspect of infection, prognosis and associated case fatality rate. Individual genetic landscapes can contribute to understand Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) burden and can give information on how to fight virus spreading and the associated severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The spread and pathogenicity of the virus have become pandemic on specific geographic areas and ethnicities. Interestingly, SARS-CoV-2 firstly emerged in East Asia and next in Europe, where it has caused higher morbidity and mortality. This is a peculiar feature of SARS-CoV-2, different from past global viral infections (i.e., SARS-1 or MERS); it shares with the previous pandemics strong age- and sex-dependent gaps in the disease outcome. The observation that the severest COVID-19 patients are more likely to have a history of hypertension, diabetes and/or cardiovascular disease and receive Renin-Angiotensin-System (RAS) inhibitor treatment raised the hypothesis that RAS-unbalancing may have a crucial role. Accordingly, we recently published a genetic hypothesis on the role of RAS-pathway genes (ACE1, rs4646994, rs1799752, rs4340, rs13447447; and ACE2, rs2285666, rs1978124, rs714205) and ABO-locus (rs495828, rs8176746) in COVID-19 prognosis, suspecting inherited genetic predispositions to be predictive of COVID-19 severity. In addition, recently, Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) found COVID-19-association signals at locus 3p21.31 (rs11385942) comprising the solute carrier SLC6A20 (Na+ and Cl- coupled transporter family) and at locus 9q34.2 (rs657152) coincident with ABO-blood group (rs8176747, rs41302905, rs8176719), and interestingly, both loci are associated to RAS-pathway. Finally, ACE1 and ACE2 haplotypes seem to provide plausible explanations for why SARS-CoV-2 have affected more heavily some ethnic groups, namely people with European ancestry, than Asians.
Keywords: ACE1; ACE2; COVID-19; RAS-pathway; SARS-CoV-2; gender-gap; prognostic markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renin-Angiotensin System: An Important Player in the Pathogenesis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 28;21(21):8038. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218038. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33126657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 mortalities strongly correlate with ACE1 I/D genotype.Gene. 2020 Oct 20;758:144944. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144944. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32628976 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19: a conundrum to decipher.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 May;24(10):5830-5841. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202005_21378. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32495923
-
COVID-19, Renin-Angiotensin System and Endothelial Dysfunction.Cells. 2020 Jul 9;9(7):1652. doi: 10.3390/cells9071652. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32660065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SNPs of ACE1 (rs4343) and ACE2 (rs2285666) genes are linked to SARS-CoV-2 infection but not with the severity of disease.Virol J. 2022 Mar 19;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01782-6. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 35305693 Free PMC article.
-
Human genetic basis of coronavirus disease 2019.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Sep 20;6(1):344. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00736-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34545062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Deletion/Deletion Genotype Is a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19: Implication and Utility for Patients Admitted to Emergency Department.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Aug 20;57(8):844. doi: 10.3390/medicina57080844. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34441050 Free PMC article.
-
Association of ACE2 Gene Variants with the Severity of COVID-19 Disease-A Prospective Observational Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 2;19(19):12622. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912622. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231922 Free PMC article.
-
ACE and ACE2 Gene Variants Are Associated With Severe Outcomes of COVID-19 in Men.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 17;13:812940. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.812940. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35250987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Kruger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.H., Nitsche A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gemmati D., Bramanti B., Serino M.L., Secchiero P., Zauli G., Tisato V. COVID-19 and Individual Genetic Susceptibility/Receptivity: Role of ACE1/ACE2 Genes, Immunity, Inflammation and Coagulation. Might the Double X-chromosome in Females Be Protective against SARS-CoV-2 Compared to the Single X-Chromosome in Males? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:3474. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103474. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sukumaran V., Veeraveedu P.T., Gurusamy N., Lakshmanan A.P., Yamaguchi K., Ma M., Suzuki K., Nagata M., Takagi R., Kodama M., et al. Olmesartan attenuates the development of heart failure after experimental autoimmune myocarditis in rats through the modulation of ANG 1-7 mas receptor. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012;351:208–219. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.12.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferrario C.M., Jessup J., Chappell M.C., Averill D.B., Brosnihan K.B., Tallant E.A., Diz D.I., Gallagher P.E. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Circulation. 2005;111:2605–2610. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.510461. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sukumaran V., Veeraveedu P.T., Lakshmanan A.P., Gurusamy N., Yamaguchi K., Ma M., Suzuki K., Kodama M., Watanabe K. Olmesartan medoxomil treatment potently improves cardiac myosin-induced dilated cardiomyopathy via the modulation of ACE-2 and ANG 1-7 mas receptor. Free Radic Res. 2012;46:850–860. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2012.684878. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

