Zinc-lysine Supplementation Mitigates Oxidative Stress in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by Preventing Phytotoxicity of Chromium, When Irrigated with Tannery Wastewater
- PMID: 32899596
- PMCID: PMC7569802
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9091145
Zinc-lysine Supplementation Mitigates Oxidative Stress in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by Preventing Phytotoxicity of Chromium, When Irrigated with Tannery Wastewater
Abstract
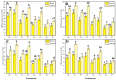
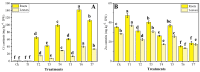
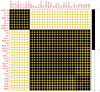
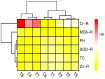
Contamination of soil and water with metals and metalloids is one of the most serious problems worldwide due to a lack of a healthy diet and food scarcity. Moreover, the cultivation of oilseed crops such as rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) with tannery wastewater could contain a large amount of toxic heavy metals [e.g., chromium (Cr)], which ultimately reduce its yield and directly influence oilseed quality. To overcome Cr toxicity in B. napus, a pot experiment was conducted to enhance plant growth and biomass by using newly introduced role of micronutrient-amino chelates [Zinc-lysine (Zn-lys)], which was irrigated with different levels [0% (control), 33%, 66%, and 100%] of tannery wastewater. According to the results of present findings, very high content of Cr in the wastewater directly affected plant growth and composition as well as gas exchange parameters, while boosting up the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and induced oxidative damage in the roots and leaves of B. napus. However, activities of antioxidants initially increased (33% of wastewater), but further addition of tannery wastewater in the soil caused a decrease in antioxidant enzymes, which also manifested by Zn content, while the conscious addition of wastewater significantly increased Cr content in the roots and shoots of B. napus. To reduce Cr toxicity in B. napus plants, exogenous supplementation of Zn-lys (10 mg/L) plays an effective role in increasing morpho-physiological attributes of B. napus and also reduces the oxidative stress in the roots and leaves of the oilseed crop (B. napus). Enhancement in different growth attributes was directly linked with increased in antioxidative enzymes while decreased uptake and accumulation of Cr content in B. napus when cultivated in wastewater with the application of Zn-lys. Zn-lys, therefore, plays a protective role in reducing the Cr toxicity of B. napus through an increase in plant growth and lowering of Cr uptake in various plant organs. However, further studies at field levels are required to explore the mechanisms of Zn-lys mediated reduction of Cr and possibly other heavy metal toxicity in plants.
Keywords: antioxidant enzymes; growth; heavy metals; micronutrient-amino chelates; oil seed crop.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kamran M., Malik Z., Parveen A., Huang L., Riaz M., Bashir S., Mustafa A., Abbasi G.H., Xue B., Ali U. Ameliorative Effects of Biochar on Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Growth and Heavy Metal Immobilization in Soil Irrigated with Untreated Wastewater. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019;39:266–281. doi: 10.1007/s00344-019-09980-3. - DOI
-
- Zaheer I.E., Ali S., Rizwan M., Abbas Z., Bukhari S.A.H., Wijaya L., Alyemeni M.N., Ahmad P. Zinc-lysine prevents chromium-induced morphological, photosynthetic, and oxidative alterations in spinach irrigated with tannery wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019;26:28951–28961. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06084-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maqbool A., Ali S., Rizwan M., Ishaque W., Rasool N., ur Rehman M.Z., Bashir A., Abid M., Wu L. Management of tannery wastewater for improving growth attributes and reducing chromium uptake in spinach through citric acid application. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018;25:10848–10856. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1352-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saleem M.H., Ali S., Hussain S., Kamran M., Chattha M.S., Ahmad S., Aqeel M., Rizwan M., Aljarba N.H., Alkahtani S. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): A Potential Candidate for Phytoremediation? Biological and Economical Points of View. Plants. 2020;9:496. doi: 10.3390/plants9040496. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

