A Higher Proportion of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) When Combined with Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) in Omega-3 Dietary Supplements Provides Higher Antioxidant Effects in Human Retinal Cells
- PMID: 32899655
- PMCID: PMC7555332
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9090828
A Higher Proportion of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) When Combined with Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) in Omega-3 Dietary Supplements Provides Higher Antioxidant Effects in Human Retinal Cells
Abstract
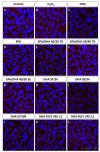
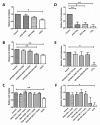
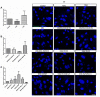
Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is a key regulator of retinal function and is directly related to the transport, delivery, and metabolism of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n3-PUFA), in the retina. Due to their functions and location, RPE cells are constantly exposed to oxidative stress. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have shown to have antioxidant effects by different mechanisms. For this reason, we designed an in vitro study to compare 10 formulations of DHA and EPA supplements from different origins and combined in different proportions, evaluating their effect on cell viability, cell proliferation, reactive oxygen species production, and cell migration using ARPE-19 cells. Furthermore, we assessed their ability to rescue RPE cells from the oxidative conditions seen in diabetic retinopathy. Our results showed that the different formulations of n3-PUFAs have a beneficial effect on cell viability and proliferation and are able to restore oxidative induced RPE damage. We observed that the n3-PUFA provided different results alone or combined in the same supplement. When combined, the best results were obtained in formulations that included a higher proportion of EPA than DHA. Moreover, n3-PUFA in the form of ethyl-esters had a worse performance when compared with triglycerides or phospholipid based formulations.
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy; docosahexaenoic acid (DHA); eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); oxidative stress; retinal pigment epithelium.
Conflict of interest statement
AGL is a consultant for Bayer, Novartis, Allergan, Thea, and Roche. The rest of the authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

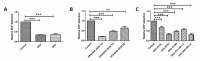


References
-
- Flaxman S.R., Bourne R.R.A., Resnikoff S., Ackland P., Braithwaite T., Cicinelli M.V., Das A., Jonas J.B., Keeffe J., Kempen J., et al. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Heal. 2017;5 doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30393-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Elisa D-NET—Connecting Diabetes Professionals Wordwide. [(accessed on 29 July 2020)]; Available online: https://d-net.idf.org.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

