Characteristics of Allergen Labelling and Precautionary Allergen Labelling in Packaged Food Products Available in Latin America
- PMID: 32899689
- PMCID: PMC7576488
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12092698
Characteristics of Allergen Labelling and Precautionary Allergen Labelling in Packaged Food Products Available in Latin America
Abstract
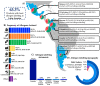
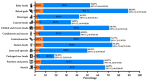
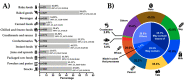
The characteristics of food allergen labelling are relevant for avoiding accidental exposure to the allergens of interest but no Latin American country has evaluated these characteristics. Our aim was to evaluate the characteristics of food allergen labelling and precautionary allergen labelling (PAL) in six Latin American countries. All data were collected directly from the supermarkets surveyed. A total of 10,254 packaged food products were analyzed, of which 63.3% (n = 6494) and 33.2% (n = 3405) featured allergen labelling and/or PAL, respectively. Most products complied with local regulations (≥87.4% for both locally produced and imported). Thirty-three types of PAL statements were detected; the most frequent was "may contain traces of…" (35.1%). Countries without regulations on the characteristics of allergen labelling had two-fold more products that contained allergens in their ingredients lists but no food allergen labelling. The use of PAL in countries that regulate it (38.2%) was as high as that in countries without PAL regulations (19.2%-44.7%). The findings suggest that the lack of regulations for the characteristics of allergen labeling increases the risk of accidental exposure to allergens of interest. Our findings also suggest that beyond regulations, a scientific approach is required for minimizing and standardizing the use of PAL.
Keywords: Latin America; allergen labelling; packaged food products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Precautionary allergen labelling following new labelling practice in Australia.J Paediatr Child Health. 2013 Apr;49(4):E306-10. doi: 10.1111/jpc.12138. Epub 2013 Mar 13. J Paediatr Child Health. 2013. PMID: 23489385
-
Food allergen labelling: "May contain" evidence from Malaysia.Food Res Int. 2018 Jun;108:455-464. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.03.068. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Food Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29735079
-
Evidence-based approaches to the application of precautionary allergen labelling: Report from two iFAAM workshops.Clin Exp Allergy. 2019 Sep;49(9):1191-1200. doi: 10.1111/cea.13464. Clin Exp Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31325393 Review.
-
A Survey of Allergic Consumers and Allergists on Precautionary Allergen Labelling: Where Do We Go from Here?Nutrients. 2025 Apr 30;17(9):1556. doi: 10.3390/nu17091556. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362864 Free PMC article.
-
Is advising food allergic patients to avoid food with precautionary allergen labelling out of date?Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Jun;16(3):272-7. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000262. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26981748 Review.
Cited by
-
The Expansion of the Hellenic Food Thesaurus; Allergens Labelling and Allergens-Free Claims on Greek Branded Food Products.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 19;14(16):3421. doi: 10.3390/nu14163421. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014926 Free PMC article.
-
Food Labeling: Analysis, Understanding, and Perception.Nutrients. 2021 Jan 19;13(1):268. doi: 10.3390/nu13010268. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33477758 Free PMC article.
-
Selected Instrumental Techniques Applied in Food and Feed: Quality, Safety and Adulteration Analysis.Foods. 2021 May 13;10(5):1081. doi: 10.3390/foods10051081. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34068197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Consumers on Food Allergy and Food Allergen Labeling: A Case of Lebanon.Foods. 2023 Feb 22;12(5):933. doi: 10.3390/foods12050933. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36900450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Codex Alimentarius Commission Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme World Health Organization . Codex Alimentarius Commission: Procedural Manual. Food & Agriculture Org.; Rome, Italy: 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

