Bayesian gamma-negative binomial modeling of single-cell RNA sequencing data
- PMID: 32900358
- PMCID: PMC7487589
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-020-06938-8
Bayesian gamma-negative binomial modeling of single-cell RNA sequencing data
Abstract
Background: Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is a powerful profiling technique at the single-cell resolution. Appropriate analysis of scRNA-seq data can characterize molecular heterogeneity and shed light into the underlying cellular process to better understand development and disease mechanisms. The unique analytic challenge is to appropriately model highly over-dispersed scRNA-seq count data with prevalent dropouts (zero counts), making zero-inflated dimensionality reduction techniques popular for scRNA-seq data analyses. Employing zero-inflated distributions, however, may place extra emphasis on zero counts, leading to potential bias when identifying the latent structure of the data.
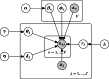
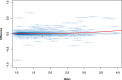
Results: In this paper, we propose a fully generative hierarchical gamma-negative binomial (hGNB) model of scRNA-seq data, obviating the need for explicitly modeling zero inflation. At the same time, hGNB can naturally account for covariate effects at both the gene and cell levels to identify complex latent representations of scRNA-seq data, without the need for commonly adopted pre-processing steps such as normalization. Efficient Bayesian model inference is derived by exploiting conditional conjugacy via novel data augmentation techniques.
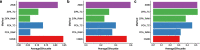
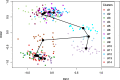
Conclusion: Experimental results on both simulated data and several real-world scRNA-seq datasets suggest that hGNB is a powerful tool for cell cluster discovery as well as cell lineage inference.
Keywords: Bayesian; Hierarchical modeling; Single-cell RNA sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shapiro E, Biezuner T, Linnarsson S. Single-cell sequencing-based technologies will revolutionize whole-organism science. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14(9):618–30. - PubMed
-
- Deng Q, Ramsköld D, Reinius B, Sandberg R. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals dynamic, random monoallelic gene expression in mammalian cells. Science. 2014;343(6167):193–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

