Mechanisms of bone development and repair
- PMID: 32901139
- PMCID: PMC7699981
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-020-00279-w
Mechanisms of bone development and repair
Abstract
Bone development occurs through a series of synchronous events that result in the formation of the body scaffold. The repair potential of bone and its surrounding microenvironment - including inflammatory, endothelial and Schwann cells - persists throughout adulthood, enabling restoration of tissue to its homeostatic functional state. The isolation of a single skeletal stem cell population through cell surface markers and the development of single-cell technologies are enabling precise elucidation of cellular activity and fate during bone repair by providing key insights into the mechanisms that maintain and regenerate bone during homeostasis and repair. Increased understanding of bone development, as well as normal and aberrant bone repair, has important therapeutic implications for the treatment of bone disease and ageing-related degeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

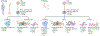

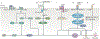
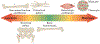
References
-
- Long F Building strong bones: molecular regulation of the osteoblast lineage. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 13, 27–38 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Garnero P, Sornay-Rendu E, Chapuy MC & Delmas PD Increased bone turnover in late postmenopausal women is a major determinant of osteoporosis. J. Bone Miner. Res 11, 337–349 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

