Mechanistic Multilayer Quantitative Model for Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics, Target Occupancy and Pharmacodynamics (PK/TO/PD) Relationship of D-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitor, TAK-831 in Mice
- PMID: 32901384
- PMCID: PMC7478952
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-020-02893-x
Mechanistic Multilayer Quantitative Model for Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics, Target Occupancy and Pharmacodynamics (PK/TO/PD) Relationship of D-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitor, TAK-831 in Mice
Abstract
Purpose: TAK-831 is a highly selective and potent inhibitor of D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) currently under clinical development for schizophrenia. In this study, a mechanistic multilayer quantitative model that parsimoniously connects pharmacokinetics (PK), target occupancy (TO) and D-serine concentrations as a pharmacodynamic (PD) readout was established in mice.
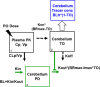
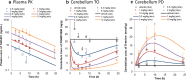
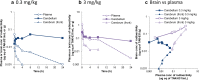
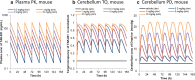
Methods: PK, TO and PD time-profiles were obtained in mice and analyzed by mechanistic binding kinetics model connected with an indirect response model in a step wise fashion. Brain distribution was investigated to elucidate a possible mechanism driving the hysteresis between PK and TO.
Results: The observed nonlinear PK/TO/PD relationship was well captured by mechanistic modeling framework within a wide dose range of TAK-831 in mice. Remarkably different brain distribution was observed between target and reference regions, suggesting that the target-mediated slow binding kinetics rather than slow penetration through the blood brain barrier caused the observed distinct kinetics between PK and TO.
Conclusion: A quantitative mechanistic model for concentration- and time-dependent nonlinear PK/TO/PD relationship was established for TAK-831 in mice with accounting for possible rate-determining process. The established mechanistic modeling framework will provide a quantitative means for multilayer biomarker-assisted clinical development in multiple central nervous system indications.
Keywords: D-amino acid oxidase inhibitor; PK/PD, multilayer quantitative model; TAK-831; target occupancy.
Figures

References
-
- Strick CA, Li C, Scott L, Harvey B, Hajos M, Steyn SJ, Piotrowski MA, James LC, Downs JT, Rago B, Becker SL, El-Kattan A, Xu Y, Ganong AH, Tingley FD, 3rd, Ramirez AD, Seymour PA, Guanowsky V, Majchrzak MJ, Fox CB, Schmidt CJ, Duplantier AJ. Modulation of NMDA receptor function by inhibition of D-amino acid oxidase in rodent brain. Neuropharmacology. 2011;61(5–6):1001–1015. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.06.029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

