Effectiveness of Amlodipine on Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive Patients in India: A Real-World, Retrospective Study from Electronic Medical Records
- PMID: 32901435
- PMCID: PMC7581658
- DOI: 10.1007/s40801-020-00211-w
Effectiveness of Amlodipine on Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive Patients in India: A Real-World, Retrospective Study from Electronic Medical Records
Abstract
Background: The effectiveness of amlodipine has been reported in clinical trials in India. However, real-world data on the effectiveness of amlodipine in India is limited.
Objective: To provide real-world evidence regarding the effectiveness of amlodipine as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs (AHDs) in Indian patients with essential hypertension.
Methods: Electronic medical record data of adult patients who were diagnosed with essential hypertension (≥ 140/90 mmHg) and were prescribed amlodipine as monotherapy or add-on therapy were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were classified based on the number of AHD classes prescribed on initiation of amlodipine. Change in systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressure from baseline was the primary endpoint. Evaluation of proportion of patients who achieved treatment goals as per 2018 European Society of Cardiology/European Society of Hypertension guidelines was the secondary endpoint. Readings were obtained before initiating amlodipine and after at least a month of therapy with amlodipine.
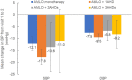
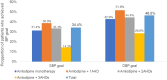
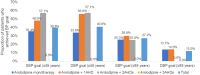
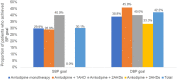
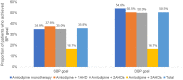
Results: Among the 462 included patients, the majority (90.7%) were on amlodipine monotherapy or amlodipine + 1AHD. Mean (95% confidence interval [CI]) change in the amlodipine monotherapy group was: SBP (- 12.1 [- 14.9, - 9.3] mmHg) and DBP (- 7.5 [- 8.9, - 6.1] mmHg) and mean (95% CI) change in the amlodipine + 1AHD group was: SBP (- 17.8 [- 21.0, - 14.6] mmHg) and DBP (- 9.5 [- 11.0, - 8.0] mmHg) (P < 0.001 for all). SBP and DBP goals were achieved by 31.4% and 42.9% of patients on amlodipine monotherapy and by 38.9% and 51.8% of patients on amlodipine + 1AHD, respectively. Among patients aged ≤ 45 years, mean (95% CI) change in the amlodipine monotherapy group was: SBP (- 11.7 [- 16.0, - 7.4] mmHg; P < 0.001) and DBP (- 7.2 [- 9.7, - 4.7] mmHg; P < 0.001) and mean (95% CI) change in the amlodipine + 1AHD group was: SBP (- 14.6 [- 21.9, - 7.3] mmHg; P < 0.05) and DBP (- 10.6 [- 14.8, - 6.4] mmHg; P < 0.01). SBP and DBP goals were achieved by 35.4% and 33.8% of patients on amlodipine monotherapy and by 48.0% and 56.0% of patients on amlodipine + 1AHD, respectively. Among patients aged ≥ 65 years, mean (95% CI) change in the amlodipine monotherapy group was: SBP (- 13.9 [- 20.2, - 7.6] mmHg; P < 0.01) and DBP (- 8.5 [- 11.4, - 5.7] mmHg; P < 0.001) and mean (95% CI) change in the amlodipine + 1AHD group was: SBP (- 22.4 [- - 28.8, - 16.0] mmHg; P < 0.001) and DBP (- 10.8 [- 14.0, - 7.6] mmHg; P < 0.001). SBP and DBP goals were achieved by 25.5% and 13.7% of patients on amlodipine monotherapy and by 29.8% and 14.0% of patients on amlodipine + 1AHD.
Conclusion: Amlodipine prescribed as monotherapy or add-on therapy during routine clinical practice significantly reduced BP in ≤ 45- and ≥ 65-year-old Indian patients with mild to moderate hypertension, emphasizing that amlodipine may be a good candidate for BP control in Indian patients with essential hypertension in these age groups.
Conflict of interest statement
MYK, SP, AM, and SM are employees of Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories and may own stock. SS is an employee of Healthplix Ltd, which received consultancy fees from Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories to perform the study. SR, JCM, BCS, and SRK are members of the advisory board for Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories.
Figures
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2017 (GBD 2017) Results. Seattle, United States: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME); 2018.
-
- Paramore LC, Halpern MT, Lapuerta P, Hurley JS, Frost FJ, Fairchild DG, et al. Impact of poorly controlled hypertension on healthcare resource utilization and cost. Am J Manag Care. 2001;7(4):389–398. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

