The LEAP Program: Quality Improvement Training to Address Team Readiness Gaps Identified by Implementation Science Findings
- PMID: 32901440
- PMCID: PMC7878618
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-020-06133-1
The LEAP Program: Quality Improvement Training to Address Team Readiness Gaps Identified by Implementation Science Findings
Abstract
Background: Integrating evidence-based innovations (EBIs) into sustained use is challenging; most implementations in health systems fail. Increasing frontline teams' quality improvement (QI) capability may increase the implementation readiness and success of EBI implementation.
Objectives: Develop a QI training program ("Learn. Engage. Act. Process." (LEAP)) and evaluate its impact on frontline obesity treatment teams to improve treatment delivered within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA).
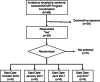
Design: This was a pre-post evaluation of the LEAP program. MOVE! coordinators (N = 68) were invited to participate in LEAP; 24 were randomly assigned to four starting times. MOVE! coordinators formed teams to work on improvement aims. Pre-post surveys assessed team organizational readiness for implementing change and self-rated QI skills. Program satisfaction, assignment completion, and aim achievement were also evaluated.
Participants: VHA facility-based MOVE! teams.
Interventions: LEAP is a 21-week QI training program. Core components include audit and feedback reports, structured curriculum, coaching and learning community, and online platform.
Main measures: Organizational readiness for implementing change (ORIC); self-rated QI skills before and after LEAP; assignment completion and aim achievement; program satisfaction.
Key results: Seventeen of 24 randomized teams participated in LEAP. Participants' self-ratings across six categories of QI skills increased after completing LEAP (p< 0.0001). The ORIC measure showed no statistically significant change overall; the change efficacy subscale marginally improved (p < 0.08), and the change commitment subscale remained the same (p = 0.66). Depending on the assignment, 35 to 100% of teams completed the assignment. Nine teams achieved their aim. Most team members were satisfied or very satisfied (81-89%) with the LEAP components, 74% intended to continue using QI methods, and 81% planned to continue improvement work.
Conclusions: LEAP is scalable and does not require travel or time away from clinical responsibilities. While QI skills improved among participating teams and most completed the work, they struggled to do so amid competing clinical priorities.
Keywords: implementation science; learning collaborative; quality improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have a conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of a virtual quality improvement training program to improve reach of weight management programs within a large health system.Health Serv Res. 2024 Dec;59 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):e14344. doi: 10.1111/1475-6773.14344. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39054798 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Continuous quality improvement at the frontline: One interdisciplinary clinical team's four-year journey after completing a virtual learning program.Learn Health Syst. 2022 Sep 27;6(4):e10345. doi: 10.1002/lrh2.10345. eCollection 2022 Oct. Learn Health Syst. 2022. PMID: 36263266 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing fidelity to evidence-based quality improvement as an implementation strategy for patient-centered medical home transformation in the Veterans Health Administration.Implement Sci. 2020 Mar 18;15(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13012-020-0979-y. Implement Sci. 2020. PMID: 32183873 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Quality Improvement Coaching on Process Outcomes in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review.J Gen Intern Med. 2022 Mar;37(4):885-899. doi: 10.1007/s11606-021-07217-2. Epub 2022 Jan 3. J Gen Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 34981354 Free PMC article.
-
Team dynamics within quality improvement teams: a scoping review.Int J Qual Health Care. 2018 Jul 1;30(6):416-422. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzy045. Int J Qual Health Care. 2018. PMID: 29617795
Cited by
-
Enhancing capability for continuous organisational improvement and learning in healthcare organisations: a systematic review of the literature 2013-2022.BMJ Open Qual. 2024 Apr 2;13(2):e002566. doi: 10.1136/bmjoq-2023-002566. BMJ Open Qual. 2024. PMID: 38569667 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of a Web-Based Tool for Shared Decision-making in Lung Cancer Screening: Mixed Methods Quality Improvement Evaluation.JMIR Hum Factors. 2022 Apr 1;9(2):e32399. doi: 10.2196/32399. JMIR Hum Factors. 2022. PMID: 35363144 Free PMC article.
-
Good practices to optimise the performance of maternal and neonatal quality improvement teams: Results from a longitudinal qualitative evaluation in South Africa, before, and during COVID-19.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 19;19(11):e0314024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314024. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39561133 Free PMC article.
-
A pragmatic context assessment tool (pCAT): using a Think Aloud method to develop an assessment of contextual barriers to change.Implement Sci Commun. 2023 Jan 11;4(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s43058-022-00380-5. Implement Sci Commun. 2023. PMID: 36631914 Free PMC article.
-
Core and modifiable components of academic detailing: demonstration of implementation strategy development, tailoring, and documentation process.Front Health Serv. 2025 Jun 3;5:1521504. doi: 10.3389/frhs.2025.1521504. eCollection 2025. Front Health Serv. 2025. PMID: 40529793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meaney M, Pung C. McKinsey global results: creating organizational transformations. McKinsey Q. 2008;7(3):1–7.
-
- Rafferty AE, Jimmieson NL, Armenakis AA. Change readiness: a multilevel review. J Manag. 2013;39(1):110–135.
-
- Balas EA, Boren SA. Managing clinical knowledge for health care improvement. Yearb Med Inform. 2000;9(01):65–70. - PubMed
-
- VA Utilization Profile FY 2016. In: Affairs USDoV, ed: National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources