Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast: Standardization of Image Acquisition and Interpretation
- PMID: 32901461
- PMCID: PMC7772373
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0093
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast: Standardization of Image Acquisition and Interpretation
Abstract
Diffusion-weighted (DW) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a rapid, unenhanced imaging technique that measures the motion of water molecules within tissues and provides information regarding the cell density and tissue microstructure. DW MRI has demonstrated the potential to improve the specificity of breast MRI, facilitate the evaluation of tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and can be employed in unenhanced MRI screening. However, standardization of the acquisition and interpretation of DW MRI is challenging. Recently, the European Society of Breast Radiology issued a consensus statement, which described the acquisition parameters and interpretation of DW MRI. The current article describes the basic principles, standardized acquisition protocols and interpretation guidelines, and the clinical applications of DW MRI in breast imaging.
Keywords: Cancer; Dense breast; Diffusion-weighted MRI; Standardization; Supplemental screening.
Copyright © 2021 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
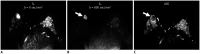

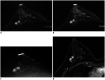
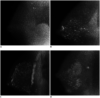
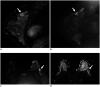
References
-
- Kriege M, Brekelmans CT, Boetes C, Besnard PE, Zonderland HM, Obdeijn IM, et al. Efficacy of MRI and mammography for breast-cancer screening in women with a familial or genetic predisposition. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:427–437. - PubMed
-
- Warner E, Plewes DB, Hill KA, Causer PA, Zubovits JT, Jong RA, et al. Surveillance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers with magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, mammography, and clinical breast examination. JAMA. 2004;292:1317–1325. - PubMed
-
- Kuhl CK, Schrading S, Leutner CC, Morakkabati-Spitz N, Wardelmann E, Fimmers R, et al. Mammography, breast ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging for surveillance of women at high familial risk for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8469–8476. - PubMed
-
- Leach MO, Boggis CR, Dixon AK, Easton DF, Eeles RA, Evans DG, et al. Screening with magnetic resonance imaging and mammography of a UK population at high familial risk of breast cancer: a prospective multicentre cohort study (MARIBS) Lancet. 2005;365:1769–1778. - PubMed
-
- Lehman CD, Blume JD, Thickman D, Bluemke DA, Pisano E, Kuhl C, et al. Added cancer yield of MRI in screening the contralateral breast of women recently diagnosed with breast cancer: results from the International Breast Magnetic Resonance Consortium (IBMC) trial. J Surg Oncol. 2005;92:9–15. discussion 15–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

