Tracking the onset date of the community spread of SARS-CoV-2 in western countries
- PMID: 32901696
- PMCID: PMC7472723
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760200183
Tracking the onset date of the community spread of SARS-CoV-2 in western countries
Abstract
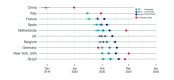
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) rapidly spread around the world during 2020, but the precise time in which the virus began to spread locally is difficult to trace for most countries. Here, we estimate the probable onset date of the community spread of SARS-CoV-2 for heavily affected countries from Western Europe and the Americas on the basis of the cumulative number of deaths reported during the early stage of the epidemic. Our results support that SARS-CoV-2 probably started to spread locally in all western countries analysed between mid-January and mid-February 2020, thus long before community transmission was officially recognised and control measures were implemented.
Figures

References
-
- Worldometer COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic. 2020. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

