MicroRNA‑195 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian carcinoma via inhibition of the CDC42/CCND1 pathway
- PMID: 32901852
- PMCID: PMC7521559
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4716
MicroRNA‑195 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian carcinoma via inhibition of the CDC42/CCND1 pathway
Abstract
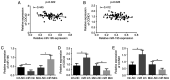
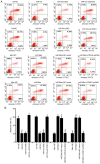
Epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC) is the most common cause of gynecological cancer mortality, and poses a threat to women. MicroRNA‑195 (miR‑195) has been reported to induce apoptosis of human OVCAR‑3 cells by inhibiting the VEGFR2/AKT pathway. However, the role of miR‑195 in EOC remains unknown. A previous study reported that cell division cycle 42 (CDC42) can serve as a target gene of miR‑195 and mediate malignant progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of miR‑195 in EOC and the regulation in CDC42/CCND1 pathway. Tissues samples and clinical materials were collected from 78 enrolled patients with EOC to analyze the expression and clinical significance of miR‑195, CDC42 and cyclin D1 (CCND1). Human EOC cell lines OVCA420, OVCAR‑3, A2780 and SKOV3 cell lines were used to assess the expression and function of miR‑195, CDC42 and CCND1 in vitro. Cell proliferation, the cell cycle and apoptosis, as well as the cell migratory and invasive abilities were detected in vitro using BrdU incorporation, colony formation, wound healing and Transwell invasion assays, along with flow cytometry. miR‑195 was downregulated, while CDC42 and CCND1 were upregulated in human EOC tissues and cells, and the aberrant expression of both was associated with increased EOC malignancy. Moreover, miR‑195 expression was negatively correlated with CDC42 and CCND1 expression levels, and negatively regulated these expression levels. Thus, it was suggested that miR‑195 functions as a tumor suppressor, but CDC42 and CCND1 act as tumor promoters based their abilities to enhance cell proliferation, cell cycle entry, migration and invasion, as well as decrease apoptosis in OVCAR‑3 cells. the present results demonstrated that miR‑195 inhibited human EOC progression by downregulating CDC42 and CCND1 expression. Furthermore, it was identified that miR‑195, CDC42 and CCND1 may be effective biomarkers for EOC diagnosis and treatment.
Figures




References
-
- Parizadeh SM, Jafarzadeh-Esfehani R, Ghandehari M, Hasanzadeh M, Parizadeh SMR, Hassanian SM, Rezaei-Kalat A, Aghabozorgi AS, Rahimi-Kakhki R, Zargaran B, et al. Circulating and tissue microRNAs as biomarkers for ovarian cancer prognosis. Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20:1447–1460. doi: 10.2174/1389450120666190708100308. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Menke K, Schwermer M, Falke K, Felenda J, Beckmann C, Stintzing F, Voigt A, Schramm A, Zuzak TJ. Taraxacum officinale extract induces antitumorigenic effects in ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2019;40:106–112.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

