Perampanel reduces paroxysmal depolarizing shift and inhibitory synaptic input in excitatory neurons to inhibit epileptic network oscillations
- PMID: 32901915
- PMCID: PMC7589018
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.15253
Perampanel reduces paroxysmal depolarizing shift and inhibitory synaptic input in excitatory neurons to inhibit epileptic network oscillations
Abstract
Background and purpose: Perampanel is a newly approved anticonvulsant uniquely targeting AMPA receptors, which mediate the most abundant form of excitatory synaptic transmission in the brain. However, the network mechanism underlying the anti-epileptic effect of the AMPAergic inhibition remains to be explored.
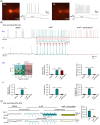
Experimental approach: The mechanism of perampanel action was studied with the basolateral amygdala network containing pyramidal-inhibitory neuronal resonators in seizure models of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and electrical kindling.
Key results: Application of either 4-AP or electrical kindling to the basolateral amygdala readily induces AMPAergic transmission-dependent reverberating activities between pyramidal-inhibitory neuronal resonators, which are chiefly characterized by burst discharges in inhibitory neurons and corresponding recurrent inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in pyramidal neurons. Perampanel reduces post-kindling "paroxysmal depolarizing shift" especially in pyramidal neurons and, counterintuitively, eliminates burst activities in inhibitory neurons and inhibitory synaptic inputs onto excitatory pyramidal neurons to result in prevention of epileptiform discharges and seizure behaviours. Intriguingly, similar effects can be obtained with not only the AMPA receptor antagonist CNQX but also the GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline, which is usually considered as a proconvulsant.
Conclusion and implications: Ictogenesis depends on the AMPA receptor-dependent recruitment of pyramidal-inhibitory neuronal network oscillations tuned by dynamic glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission. The anticonvulsant effect of perampanel then stems from disruption of the coordinated network activities rather than simply decreased neuronal excitability or excitatory transmission. Positive or negative modulation of epileptic network reverberations may be pro-ictogenic or anti-ictogenic, respectively, constituting a more applicable rationale for the therapy against seizures.
Keywords: AMPA receptors; GABAergic transmission; epileptic seizures; glutamatergic transmission; perampanel.
© 2020 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
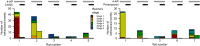



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOST107-2311-B-182-004/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- MOST108-2311-B-182-001/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- MOST108-2321-B-007-003-MY2/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- MOST109-2320-B-182-006/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- MOST 108-2321-B-007-003-MY2/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

