Oxaliplatin- and docetaxel-induced polyneuropathy: clinical and neurophysiological characteristics
- PMID: 32902058
- PMCID: PMC7756561
- DOI: 10.1111/jns.12413
Oxaliplatin- and docetaxel-induced polyneuropathy: clinical and neurophysiological characteristics
Abstract
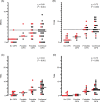
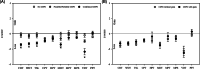
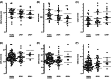
The aim of this study was to evaluate the presence and characterization of chemotherapy-induced neuropathy (CIPN) and neuropathic pain 5 years after adjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel or oxaliplatin. Patients from an ongoing prospective study, who had received adjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel or oxaliplatin in 2011 to 2012 were invited to participate. The patients underwent a thorough examination with interview, neurological examination, questionnaires, assessment tools, nerve conduction studies (NCS), quantitative sensory testing, MScan motor unit number estimation (MUNE), and corneal confocal microscopy (CCM). Patients were divided into no, possible, probable, and confirmed CIPN. Out of the 132 eligible patients, 63 agreed to participate: 28 had received docetaxel and 35 had received oxaliplatin. Forty-one percent had confirmed CIPN, 34% possible or probable CIPN, and 22% did not have CIPN. The CIPN was characterized mainly by sensory nerve fiber loss, with a more pronounced large fiber than small fiber loss but also some motor fiber loss identified on NCS and MUNE. In general, patients had mild neuropathy with relatively low scores on assessment tools and no association with mood and quality of life. CCM was not useful as a diagnostic tool. Of the patients with probable or confirmed CIPN, 30% experienced pain, which was most often mild, but still interfered moderately with daily life in 20% to 25% and was associated with lower quality of life. In conclusion CIPN was confirmed in 41% 5 years after chemotherapy. The neuropathy was generally mild, but in patients with neuropathic pain it was associated with lower quality of life.
Keywords: assessment tools; chemotherapy; corneal confocal microscopy; large fiber neuropathy; motor unit number estimation; nerve conduction study; neuropathic pain; neuropathy; pain; small fiber neuropathy.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Peripheral Nerve Society.
Figures

References
-
- Hausheer FH, Schilsky RL, Bain S, Berghorn EJ, Lieberman F. Diagnosis, management, and evaluation of chemotherapy‐induced peripheral neuropathy. Semin Oncol. 2006;33:15‐49. - PubMed
-
- Andre T, Vernerey D, Mineur L, et al. 3 versus 6 months of oxaliplatin‐based adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with stage III colon cancer: disease‐free survival results from a randomized, open‐label, international duration evaluation of adjuvant (IDEA) France, phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1469‐1477. - PubMed
-
- Velasco R, Bruna J, Briani C, et al. Early predictors of oxaliplatin‐induced cumulative neuropathy in colorectal cancer patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014;85:392‐398. - PubMed
-
- Kandula T, Farrar MA, Kiernan MC, et al. Neurophysiological and clinical outcomes in chemotherapy‐induced neuropathy in cancer. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128:1166‐1175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

