Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on acute stroke reperfusion therapy: data from the Lyon Stroke Center Network
- PMID: 32902732
- PMCID: PMC7479751
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-020-10199-6
Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on acute stroke reperfusion therapy: data from the Lyon Stroke Center Network
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic would have particularly affected acute stroke care. However, its impact is clearly inherent to the local stroke network conditions. We aimed to assess the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on acute stroke care in the Lyon comprehensive stroke center during this period.
Methods: We conducted a prospective data collection of patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) treated with intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) and/or mechanical thrombectomy (MT) during the COVID-19 period (from 29/02/2020 to 10/05/2020) and a control period (from 29/02/2019 to 10/05/2019). The volume of reperfusion therapies and pre and intra-hospital delays were compared during both periods.
Results: A total of 208 patients were included. The volume of IVT significantly decreased during the COVID-period [55 (54.5%) vs 74 (69.2%); p = 0.03]. The volume of MT remains stable over the two periods [72 (71.3%) vs 65 (60.8%); p = 0.14], but the door-to-groin puncture time increased in patients transferred for MT (237 [187-339] vs 210 [163-260]; p < 0.01). The daily number of Emergency Medical Dispatch calls considerably increased (1502 [1133-2238] vs 1023 [960-1410]; p < 0.01).
Conclusions: Our study showed a decrease in the volume of IVT, whereas the volume of MT remained stable although intra-hospital delays increased for transferred patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. These results contrast in part with the national surveys and suggest that the impact of the pandemic may depend on local stroke care networks.
Keywords: COVID-19; Stroke; Thrombectomy; Thrombolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
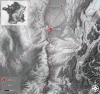

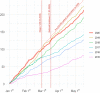
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

