Implications of flavonoids as potential modulators of cancer neovascularity
- PMID: 32902794
- PMCID: PMC11804697
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-020-03383-8
Implications of flavonoids as potential modulators of cancer neovascularity
Abstract
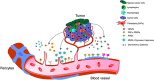
Purpose: The formation of new blood vessels from previous ones, angiogenesis, is critical in tissue repair, expansion or remodeling in physiological processes and in various pathologies including cancer. Despite that, the development of anti-angiogenic drugs has great potential as the treatment of cancer faces many problems such as development of the resistance to treatment or an improperly selected therapy approach. An evaluation of predictive markers in personalized medicine could significantly improve treatment outcomes in many patients.
Methods: This comprehensive review emphasizes the anticancer potential of flavonoids mediated by their anti-angiogenic efficacy evaluated in current preclinical and clinical cancer research.
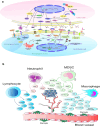
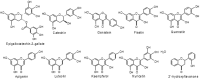
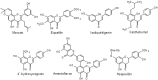
Results and conclusion: Flavonoids are important groups of phytochemicals present in common diet. Flavonoids show significant anticancer effects. The anti-angiogenic effects of flavonoids are currently a widely discussed topic of preclinical cancer research. Flavonoids are able to regulate the process of tumor angiogenesis through modulation of signaling molecules such as VEGF, MMPs, ILs, HIF or others. However, the evaluation of the anti-angiogenic potential of flavonoids within the clinical studies is not frequently discussed and is still of significant scientific interest.
Keywords: Anti-cancer therapy; Cancer; Flavonoids; Neovascularity; Tumor angiogenesis; VEGF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdollahi A, Folkman J (2010) Evading tumor evasion: current concepts and perspectives of anti-angiogenic cancer therapy. Drug Resist Update 13:16–28 - PubMed
-
- Adair TH, Montani JP (2010) Angiogenesis. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences, San Rafael - PubMed
-
- Aiello P, Consalvi S, Poce G, Raguzzini A, Toti E, Palmery M, Biava M, Bernardi M, Kamal MA, Perry G, Peluso I (2019) Dietary flavonoids: nano delivery and nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 2019:1044-579X(19)30217-2. - PubMed
-
- Amiri-Kordestani L, Tan AR, Swain SM (2012) Pazopanib for the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 21:217–225 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

