Molecular adaptation to calsequestrin 2 (CASQ2) point mutations leading to catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT): comparative analysis of R33Q and D307H mutants
- PMID: 32902830
- PMCID: PMC7666291
- DOI: 10.1007/s10974-020-09587-2
Molecular adaptation to calsequestrin 2 (CASQ2) point mutations leading to catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT): comparative analysis of R33Q and D307H mutants
Abstract
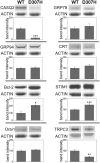
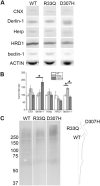
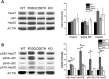
Homozygous calsequestrin 2 (CASQ2) point mutations leads to catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: a common pathogenetic feature appears to be the drastic reduction of mutant CASQ2 in spite of normal transcription. Comparative biochemical analysis of R33Q and D307H knock in mutant mice identifies different pathogenetic mechanisms for CASQ2 degradation and different molecular adaptive mechanisms. In particular, each CASQ2 point mutation evokes specific adaptive cellular and molecular processes in each of the four adaptive pathways investigated. Thus, similar clinical phenotypes and identical cellular mechanism for cardiac arrhythmia might imply different molecular adaptive mechanisms.
Keywords: CASQ2 mutations; Cathecolaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia; Degradative pathways; Small heat shock proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Hassnan ZN, Tulbah S, Al-Manea W, Al-Fayyadh M. The phenotype of a CASQ2 mutation in a Saudi family with catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013;36:e140–e142. - PubMed
-
- Bakthisaran R, Tangirala R, Rao CM. Small heat shock proteins: Role in cellular functions and pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1854:291–319. - PubMed
-
- Bonilla IM, Belevych A, Baine S, Stepanov A, Mezache L, Bodnar T, Liu B, Volpe P, Priori SG, Weisleder N, Sakuta G, Carnes CA, Radwanski PB, Veeraraghavan R, Gyorke S. Enhancement of cardiac store operated calcium entry (SOCE) within novel intercalated disk microdomains in arrhythmic disease. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10179. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brundel BJ, Henning RH, Ke L, van Gelder IC, Crijns HJ, Kampinga HH. Heat shock protein upregulation protects against pacinginduced myolysis in HL-1 atrial myocytes and in human atrial fibrillation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006;41:555–562. - PubMed
-
- Bullard B, Ferguson C, Minajeva A, Leake MC, Gautel M, Labeit D, Ding L, Labeit S, Horwitz J, Leonard KR, Linke WA. Association of the chaperone alphaB-crystallin with titin in heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:7917–7924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

