The use of behaviour management techniques amongst paediatric dentists working in the Arabian region: a cross-sectional survey study
- PMID: 32902832
- PMCID: PMC8213577
- DOI: 10.1007/s40368-020-00560-8
The use of behaviour management techniques amongst paediatric dentists working in the Arabian region: a cross-sectional survey study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The use of behaviour management techniques amongst paediatric dentists working in the Arabian region: a cross-sectional survey study.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022 Jun;23(3):497. doi: 10.1007/s40368-022-00713-x. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35604572 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: The purposes of this study were to investigate paediatric dental practitioners' training and confidence in using dental behaviour management techniques in the Arabian region and to assess the factors influencing the application of advanced behaviour management techniques.
Methods: An online questionnaire was distributed to paediatric dental practitioners in the Arabian region. Data were analysed using descriptive statistics and Pearson Chi Square.
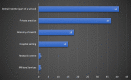
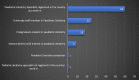
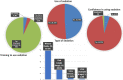
Results: A total of 113 responses were obtained. Of these, the majority were from Egypt (45%, n = 51). Just over half of the respondents were registered as specialists at the country where they were practicing paediatric dentistry (53%, n = 60). The use of behaviour management techniques varied amongst participants with tell-show-do (95%, n = 107) and positive reinforcement (89%, n = 101) being the most routinely used techniques. The majority of participants reported using voice control (83%) and parental separation (68%) techniques. Hand over mouth exercise (HOME) was only used by 24% (n = 27) of participants, whilst just over half of the participants, 53%, reported using protective stabilisation. A significant association was shown between country of practice, country of obtaining paediatric dental training, speciality status and the use of advanced behaviour management techniques, whilst confidence in using HOME and sedation were associated with work setting and country of practice, respectively.
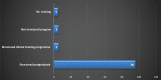
Conclusion: The use of advanced behaviour management techniques was found to be high amongst respondents in the Arabian region. The lack of training in using these techniques, however, is of concern. Further assessment of the factors affecting the use of and confidence in applying advanced behaviour management techniques in the Arabian region is needed.
Keywords: Arabian region; Behaviour management; Children; Paediatric dentists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no affiliation or involvement in an organisation or entity with a financial or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Abushal MS, Adenubi JO. Attitudes of Saudi parents toward behavior management techniques in pediatric dentistry. J Dent Child (Chic) 2003;70:104–110. - PubMed
-
- Adair S, Waller J, Schafer T, Rockman R. A survey of members of the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry on their use of behavior management techniques. Pediatr Dent. 2004;26:159–166. - PubMed
-
- AlGharebi S, Al-Halabi M, Mawlood K, Khamis AH, Hussein I. Children’s dental anxiety (self and proxy reported) and its association with dental behaviour in a postgraduate dental hospital. Eur Archiv Paediatr Dentistry. 2020;13:1–2. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Behavior Guidance for the Pediatric Dental Patient. Pediatr Dent. 2017;39:246–259. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

