Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 and the deduction effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in pregnancy
- PMID: 32902940
- PMCID: PMC7434025
- DOI: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000362
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 and the deduction effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in pregnancy
Abstract
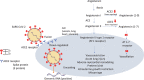
The 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV, later named SARS-CoV-2) is a pandemic disease worldwide. The spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is continuing at a rapid speed. Till May 4, 2020, there have been 3,407,747 confirmed cases and 238,198 deaths globally. The common symptoms in pregnant women are fever, cough, and dyspnea. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) has transient overexpression and increased activity during pregnancy, which is now confirmed as the receptor of SARS-CoV-2 and plays essential roles in human infection and transmission. There is no evidence that pregnant women are more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2. To date, there is no valid medication or vaccination. The immune suppression or modulation during pregnancy increases the risk of severe pneumonia. Remdesivir is an antiviral medication targeting ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis that has clinical improvement in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2. Chloroquine is controversial in its effectiveness and safety to treat SARS-CoV-2. Remdesivir is safe in pregnancy. Chloroquine has not been formally assigned to a pregnancy category by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The management strategy includes monitoring fetal heart rate and uterine contractions; early oxygenation if O2 saturation is less than 95%; empiric antibiotics for prevention of secondary infection; corticosteroid to treat maternal SARS-CoV-2 disease routinely is not suggested, only for fetal lung maturation in selected cases; and consideration of delivery is according to the obstetric indication, gestational age, and severity of the disease. During epidemics, delivery at 32-34 weeks is considered. The indication for the Cesarean section should be flexible to minimize the risk of infection during the delivery. The newborn should be in isolation ward immediately after birth; breastfeeding is not contraindicated but should avoid direct transmission infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to the subject matter or materials discussed in this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of the susceptibility to COVID-19 in pregnancy and recommendations on potential drug screening.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Jul;39(7):1209-1220. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-03897-6. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32328850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of coronavirus infection (SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV) during pregnancy and the possibility of vertical maternal-fetal transmission: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2020 Sep 4;25(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s40001-020-00439-w. Eur J Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32887660 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and pregnancy.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun;222(6):521-531. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.03.021. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32217113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers and the COVID-19 Pandemic: At Present There Is No Evidence to Abandon Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers.Hypertension. 2020 Jun;75(6):1382-1385. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15082. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32208987 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2.Circ Res. 2020 May 8;126(10):1456-1474. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32264791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Treatments against COVID-19 in Pregnant Women.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 24;10(21):4896. doi: 10.3390/jcm10214896. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34768416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fraxinol attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury by equilibrating ACE-Ang II-AT1R and ACE2-Ang (1-7)-Mas and inhibiting NLRP3.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):979-989. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2067571. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35588103 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal and fetal outcomes of the pregnant woman with COVID-19: The first case report in Taiwan.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Sep;60(5):942-944. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2021.07.045. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 34507681 Free PMC article.
-
A symptomatic near-term pregnant woman recovered from SARS-CoV-2 infection.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Sep;60(5):945-948. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2021.07.046. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 34507682 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy and COVID-19: high or low risk of vertical transmission.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Aug;23(4):957-967. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00907-z. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36251144 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

