Prospective STAR-Guided Ablation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Using Sequential Mapping With Multipolar Catheters
- PMID: 32903033
- PMCID: PMC7566307
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCEP.120.008824
Prospective STAR-Guided Ablation in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Using Sequential Mapping With Multipolar Catheters
Abstract
Background: A novel stochastic trajectory analysis of ranked signals (STAR) mapping approach to guide atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation using basket catheters recently showed high rates of AF termination and subsequent freedom from AF.
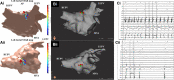
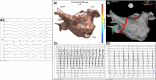
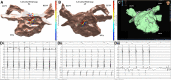
Methods: This study aimed to determine whether STAR mapping using sequential recordings from conventional pulmonary vein mapping catheters could achieve similar results. Patients with persistent AF<2 years were included. Following pulmonary vein isolation AF drivers (AFDs) were identified on sequential STAR maps created with PentaRay, IntellaMap Orion, or Advisor HD Grid catheters. Patients had a minimum of 10 multipolar recordings of 30 seconds each. These were processed in real-time and AFDs were targeted with ablation. An ablation response was defined as AF termination or cycle length slowing ≥30 ms.
Results: Thirty patients were included (62.4±7.8 years old, AF duration 14.1±4.3 months) of which 3 had AF terminated on pulmonary vein isolation, leaving 27 patients that underwent STAR-guided AFD ablation. Eighty-three potential AFDs were identified (3.1±1.1 per patient) of which 70 were targeted with ablation (2.6±1.2 per patient). An ablation response was seen at 54 AFDs (77.1% of AFDs; 21 AF termination and 33 cycle length slowing) and occurred in all 27 patients. No complications occurred. At 17.3±10.1 months, 22 out of 27 (81.5%) patients undergoing STAR-guided ablation were free from AF/atrial tachycardia off antiarrhythmic drugs.
Conclusions: STAR-guided AFD ablation through sequential mapping with a multipolar catheter effectively achieved an ablation response in all patients. AF terminated in a majority of patients, with a high freedom from AF/atrial tachycardia off antiarrhythmic drugs at long-term follow-up. Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT02950844.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; catheter ablation; coronary sinus; pulmonary vein; tachycardia.
Figures



References
-
- Haissaguerre M, Hocini M, Denis A, Shah AJ, Komatsu Y, Yamashita S, Daly M, Amraoui S, Zellerhoff S, Picat MQ, et al. Driver domains in persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2014; 130:530–538. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005421 - PubMed
-
- Knecht S, Sohal M, Deisenhofer I, Albenque JP, Arentz T, Neumann T, Cauchemez B, Duytschaever M, Ramoul K, Verbeet T, et al. Multicentre evaluation of non-invasive biatrial mapping for persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: the AFACART study. Europace. 2017; 19:1302–1309. doi: 10.1093/europace/euw168 - PubMed
-
- Narayan SM, Baykaner T, Clopton P, Schricker A, Lalani GG, Krummen DE, Shivkumar K, Miller JM. Ablation of rotor and focal sources reduces late recurrence of atrial fibrillation compared with trigger ablation alone: extended follow-up of the CONFIRM trial (Conventional Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation With or Without Focal Impulse and Rotor Modulation). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63:1761–1768. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.543 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buch E, Share M, Tung R, Benharash P, Sharma P, Koneru J, Mandapati R, Ellenbogen KA, Shivkumar K. Long-term clinical outcomes of focal impulse and rotor modulation for treatment of atrial fibrillation: a multicenter experience. Heart Rhythm. 2016; 13:636–641. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.10.031 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Honarbakhsh S, Schilling RJ, Dhillon G, Ullah W, Keating E, Providencia R, Chow A, Earley MJ, Hunter RJ. A novel mapping system for panoramic mapping of the left atrium: application to detect and characterize localized sources maintaining atrial fibrillation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018; 4:124–134. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2017.09.177 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

