Changes in a Cone Opsin Repertoire Affect Color-Dependent Social Behavior in Medaka but Not Behavioral Photosensitivity
- PMID: 32903371
- PMCID: PMC7434946
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00801
Changes in a Cone Opsin Repertoire Affect Color-Dependent Social Behavior in Medaka but Not Behavioral Photosensitivity
Abstract
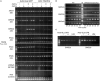
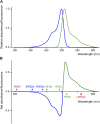
Common ancestors of vertebrates had four types of cone opsins: short-wavelength sensitive 1 (SWS1), SWS2, rhodopsin 2 (RH2), and long-wavelength sensitive (LWS) types. Whereas fish and birds retain all the types, mammals have lost two of them (SWS2 and RH2) possibly because of their nocturnal lifestyle during the Mesozoic Era. Considering that the loss of cone opsin types causes so-called color blindness in humans (e.g., protanopia), the ability to discriminate color by trichromatic humans could be lower than that in potentially tetrachromatic birds and fish. Behavioral studies using color-blind (cone opsin-knockout) animals would be helpful to address such questions, but it is only recently that the genome-editing technologies have opened up this pathway. Using medaka as a model, we introduced frameshift mutations in SWS2 (SWS2a and/or SWS2b) after detailed characterization of the loci in silico, which unveiled the existence of a GC-AG intron and non-optic expressed-sequence-tags (ESTs) that include SWS2a in part. Transcripts from the mutated SWS2 loci are commonly reduced, suggesting that the SWS2a/b-double mutants could produce, if any, severely truncated (likely dysfunctional) SWS2s in small amounts. The mutants exhibited weakened body color preferences during mate choice. However, the optomotor response (OMR) test under monochromatic light revealed that the mutants had no defect in spectral sensitivity, even at the absorbance maxima (λmax) of SWS2s. Evolutionary diversification of cone opsins has often been discussed in relation to adaptation to dominating light in habitats (i.e., changes in the repertoire or λmax are for increasing sensitivity to the dominating light). However, the present results seem to provide empirical evidence showing that acquiring or losing a type of cone opsin (or changes in λmax) need not substantially affect photopic or mesopic sensitivity. Other points of view, such as color discrimination of species-specific mates/preys/predators against habitat-specific backgrounds, may be necessary to understand why cone opsin repertories are so various among animals.
Keywords: color discrimination; medaka (Oryzias lapites); reverse genetics; sensory drive; short wavelength sensitive gene; spectral sensitivity.
Copyright © 2020 Kanazawa, Goto, Harada, Takimoto, Sasaki, Uchikawa, Kamei, Matsuo and Fukamachi.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

