Human α-Defensin-5 Efficiently Neutralizes Clostridioides difficile Toxins TcdA, TcdB, and CDT
- PMID: 32903430
- PMCID: PMC7435013
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01204
Human α-Defensin-5 Efficiently Neutralizes Clostridioides difficile Toxins TcdA, TcdB, and CDT
Abstract
Infections with the pathogenic bacterium Clostridioides (C.) difficile are coming more into focus, in particular in hospitalized patients after antibiotic treatment. C. difficile produces the exotoxins TcdA and TcdB. Since some years, hypervirulent strains are described, which produce in addition the binary actin ADP-ribosylating toxin CDT. These strains are associated with more severe clinical presentations and increased morbidity and frequency. Once in the cytosol of their target cells, the catalytic domains of TcdA and TcdB glucosylate and thereby inactivate small Rho-GTPases whereas the enzyme subunit of CDT ADP-ribosylates G-actin. Thus, enzymatic activity of the toxins leads to destruction of the cytoskeleton and breakdown of the epidermal gut barrier integrity. This causes clinical symptoms ranging from mild diarrhea to life-threatening pseudomembranous colitis. Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of the secreted toxins is of peculiar medical interest. Here, we investigated the neutralizing effect of the human antimicrobial peptide α-defensin-5 toward TcdA, TcdB, and CDT in human cells. The toxin-neutralizing effects of α-defensin-5 toward TcdA, TcdB, and CDT as well as their medically relevant combination were demonstrated by analyzing toxins-induced changes in cell morphology, intracellular substrate modification, and decrease of trans-epithelial electrical resistance. For TcdA, the underlying mode of inhibition is most likely based on the formation of inactive toxin-defensin-aggregates whereas for CDT, the binding- and transport-component might be influenced. The application of α-defensin-5 delayed intoxication of cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Due to its effect on the toxins, α-defensin-5 should be considered as a candidate to treat severe C. difficile-associated diseases.
Keywords: AB-type protein toxins; C. difficile infection; binary actin ADP-ribosylating toxin; large clostridial glucosylating toxins; toxin inhibitor.
Copyright © 2020 Korbmacher, Fischer, Landenberger, Papatheodorou, Aktories and Barth.
Figures
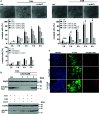
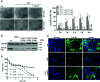
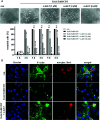
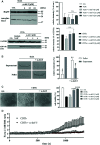
References
-
- Alpha Defensin - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/alpha-defensin (Accessed March 19, 2020).
-
- Bachmeyer C., Benz R., Barth H., Aktories K., Gilbert M., Popoff M. R. (2001). Interaction of Clostridium botulinum C2 toxin with lipid bilayer membranes and Vero cells: inhibition of channel function by chloroquine and related compounds in vitro and intoxification in vivo. FASEB J. 15, 1658–1660. 10.1096/fj.00-0671fje - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

