Polymicrobial Sepsis Impairs Antigen-Specific Memory CD4 T Cell-Mediated Immunity
- PMID: 32903436
- PMCID: PMC7435018
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01786
Polymicrobial Sepsis Impairs Antigen-Specific Memory CD4 T Cell-Mediated Immunity
Abstract
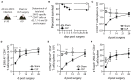
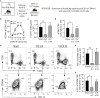
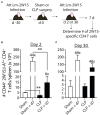
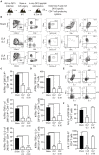
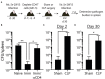
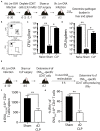
Patients who survive sepsis display prolonged immune dysfunction and heightened risk of secondary infection. CD4 T cells support a variety of cells required for protective immunity, and perturbations to the CD4 T cell compartment can decrease overall immune system fitness. Using the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) mouse model of sepsis, we investigated the impact of sepsis on endogenous Ag-specific memory CD4 T cells generated in C57BL/6 (B6) mice infected with attenuated Listeria monocytogenes (Lm) expressing the I-Ab-restricted 2W1S epitope (Lm-2W). The number of 2W1S-specific memory CD4 T cells was significantly reduced on day 2 after sepsis induction, but recovered by day 14. In contrast to the transient numerical change, the 2W1S-specific memory CD4 T cells displayed prolonged functional impairment after sepsis, evidenced by a reduced recall response (proliferation and effector cytokine production) after restimulation with cognate Ag. To define the extent to which the observed functional impairments in the memory CD4 T cells impacts protection to secondary infection, B6 mice were infected with attenuated Salmonella enterica-2W (Se-2W) 30 days before sham or CLP surgery, and then challenged with virulent Se-2W after surgery. Pathogen burden was significantly higher in the CLP-treated mice compared to shams. Similar reductions in functional capacity and protection were noted for the endogenous OVA323-specific memory CD4 T cell population in sepsis survivors upon Lm-OVA challenge. Our data collectively show CLP-induced sepsis alters the number and function of Ag-specific memory CD4 T cells, which contributes (in part) to the characteristic long-lasting immunoparalysis seen after sepsis.
Keywords: CD4 T cells; IFN-gamma; immune suppression; memory; sepsis.
Copyright © 2020 Sjaastad, Kucaba, Dileepan, Swanson, Dail, Cabrera-Perez, Murphy, Badovinac and Griffith.
Figures

References
-
- Shankar-Hari M, Phillips GS, Levy ML, Seymour CW, Liu VX, Deutschman CS, et al. Developing a new definition and assessing new clinical criteria for septic shock: for the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315:775–87. 10.1001/jama.2016.0289 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brun-Buisson C, Doyon F, Carlet J, Dellamonica P, Gouin F, Lepoutre A, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults. A multicenter prospective study in intensive care units French ICU Group for Severe Sepsis. JAMA. (1995) 274:968–74. 10.1001/jama.1995.03530120060042 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

