gC1qR/HABP1/p32 Is a Potential New Therapeutic Target Against Mesothelioma
- PMID: 32903438
- PMCID: PMC7435067
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01413
gC1qR/HABP1/p32 Is a Potential New Therapeutic Target Against Mesothelioma
Abstract
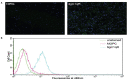
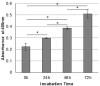
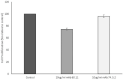
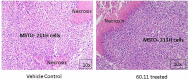
Mesothelioma is an aggressive cancer of the serous membranes with poor prognosis despite combination therapy consisting of surgery, radiotherapy, and platinum-based chemotherapy. Targeted therapies, including immunotherapies, have reported limited success, suggesting the need for additional therapeutic targets. This study investigates a potential new therapeutic target, gC1qR/HABP1/p32 (gC1qR), which is overexpressed in all morphologic subtypes of mesothelioma. gC1qR is a complement receptor that is associated with several cellular functions, including cell proliferation and angiogenesis. In vitro and in vivo experiments were conducted to test the hypothesis that targeting gC1qR with a specific gC1qR monoclonal antibody 60.11 reduces mesothelioma tumor growth, using the biphasic mesothelioma cell line MSTO-211H (MSTO). In vitro studies demonstrate cell surface and extracellular gC1qR expression by MSTO cells, and a modest 25.3 ± 1.8% (n = 4) reduction in cell proliferation by the gC1qR blocking 60.11 antibody. This inhibition was specific for targeting the C1q binding domain of gC1qR at aa 76-93, as a separate monoclonal antibody 74.5.2, directed against amino acids 204-218, had no discernable effect. In vivo studies, using a murine orthotopic xenotransplant model, demonstrated an even greater reduction in MSTO tumor growth (50% inhibition) in mice treated with the 60.11 antibody compared to controls. Immunohistochemical studies of resected tumors revealed increased cellular apoptosis by caspase 3 and TUNEL staining, in 60.11 treated tumors compared to controls, as well as impaired angiogenesis by decreased CD31 staining. Taken together, these data identify gC1qR as a potential new therapeutic target against mesothelioma with both antiproliferative and antiangiogenic properties.
Keywords: complement; gC1qR/HABP1/p32; mesothelioma; monoclonal antibody therapy; therapeutic target.
Copyright © 2020 Peerschke, Stier, Li, Kandov, de Stanchina, Chang, Xiong, Manova-Todorova, Fan, Barlas, Ghebrehiwet and Adusumilli.
Figures

References
-
- Krug LM, Pass HI, Rusch VW, Kindler HL, Sugarbaker DJ, Rosenzweig KE, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of neoadjuvant pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by extrapleural pneumonectomy and radiation for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol. (2009) 27:3007–13. 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.3943 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

