The Immune Modulating Properties of Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells
- PMID: 32903532
- PMCID: PMC7438542
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01556
The Immune Modulating Properties of Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells
Abstract
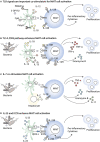
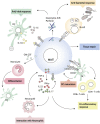
Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are unconventional T lymphocytes that express a semi-invariant T cell receptor (TCR) recognizing microbial vitamin B metabolites presented by the highly conserved major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I like molecule, MR1. The vitamin B metabolites are produced by several commensal and pathogenic bacteria and yeast, but not viruses. Nevertheless, viral infections can trigger MAIT cell activation in a TCR-independent manner, through the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). MAIT cells belong to the innate like T family of cells with a memory phenotype, which allows them to rapidly release Interferon (IFN)-γ, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and in some circumstances Interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-10, exerting an immunomodulatory role on the ensuing immune response, akin to iNKT cells and γδ T cells. Recent studies implicate MAIT cells in a variety of inflammatory, autoimmune diseases, and in cancer. In addition, through the analysis of the transcriptome of MAIT cells activated in different experimental conditions, an important function in tissue repair and control of immune homeostasis has emerged, shared with other innate-like T cells. In this review, we discuss these recent findings, focussing on the understanding of the molecular mechanisms underpinning MAIT cell activation and effector function in health and disease, which ultimately will aid in clinically harnessing this unique, not donor-restricted cell subtype.
Keywords: MAIT cells; TCR-dependent; TCR-independent; dendritic cell maturation; inflammation; tissue repair.
Copyright © 2020 Ioannidis, Cerundolo and Salio.
Figures
References
-
- Porcelli S, Yockey CE, Brenner MB, Balk SP. Analysis of T cell antigen receptor (TCR) expression by human peripheral blood CD4-8- alpha/beta T cells demonstrates preferential use of several V beta genes and an invariant TCR alpha chain. J Exp Med. (1993) 178:1–16. 10.1084/jem.178.1.1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tilloy F, Treiner E, Park SH, Garcia C, Lemonnier F, de la Salle H, et al. An invariant T cell receptor alpha chain defines a novel TAP-independent major histocompatibility complex class Ib-restricted alpha/beta T cell subpopulation in mammals. J Exp Med. (1999) 189:1907–21. 10.1084/jem.189.12.1907 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

