Immunomodulatory Drugs in the Management of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32903555
- PMCID: PMC7438578
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01844
Immunomodulatory Drugs in the Management of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
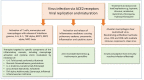
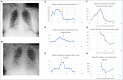
With the onset of the global pandemic in 2020 of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), there has been increasing research activity around certain disease-modifying drugs that are used for the management of inflammatory disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthrosis, psoriatic arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and inflammatory bowel disease for managing coronavirus symptoms. In the conditions mentioned, many people are on long-term treatment with agents including hydroxychloroquine, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) inhibitor drugs, other biologic agents such as monoclonal antibodies to IL-6 and Janus kinase inhibitors including baricitinib and tofacitinib, which are used to control inflammatory responses in their respective auto-immune condition. There is emerging data that immunomodulatory drugs could be protective at reducing certain features of SARS-CoV-2 and improving recovery. In addition, it is important to understand if subjects being treated with the immunomodulatory agents described have a less severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, as they are deemed some protection from their immunomodulatory treatment, or if they develop infections similar to non-immunocompromised patients. There is a huge unmet clinical need to advise patients responsibly about whether they should remain on their immunomodulatory treatment or not in light of Covid-19 infection. In this article we will discuss potential treatment options for SARS-CoV-2 using immunomodulatory drugs and at what stage of the condition they may be beneficial. Viable treatment options during the global coronavirus pandemic are a much-needed and an intensely active area of research.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; biologics; cytokines; hyperinflammation; immunomodulators.
Copyright © 2020 Burrage, Koushesh and Sofat.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

