Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles: A Novel Nanomaterial for Various Medical Applications and Biological Activities
- PMID: 32903562
- PMCID: PMC7438450
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00990
Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles: A Novel Nanomaterial for Various Medical Applications and Biological Activities
Abstract
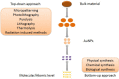
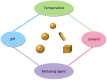
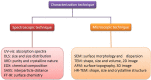
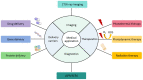
Nanotechnology has become a trending area in science and has made great advances with the development of functional, engineered nanoparticles. Various metal nanoparticles have been widely exploited for a wide range of medical applications. Among them, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are widely reported to guide an impressive resurgence and are highly remarkable. AuNPs, with their multiple, unique functional properties, and easy of synthesis, have attracted extensive attention. Their intrinsic features (optics, electronics, and physicochemical characteristics) can be altered by changing the characterization of the nanoparticles, such as shape, size and aspect ratio. They can be applied to a wide range of medical applications, including drug and gene delivery, photothermal therapy (PTT), photodynamic therapy (PDT) and radiation therapy (RT), diagnosis, X-ray imaging, computed tomography (CT) and other biological activities. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no comprehensive review that summarized the applications of AuNPs in the medical field. Therefore, in this article we systematically review the methods of synthesis, the modification and characterization techniques of AuNPs, medical applications, and some biological activities of AuNPs, to provide a reference for future studies.
Keywords: AuNPs; biological activities; characterization; medical applications; modification; synthesis.
Copyright © 2020 Hu, Zhang, Ding, Liu and Zhao.
Figures







References
-
- Ahn S., Singh P., Jang M., Kim Y. J., Castro-Aceituno V., Simu S. Y., et al. (2017). Gold nanoflowers synthesized using Acanthopanacis cortex extract inhibit inflammatory mediators in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages via NF-κB and AP-1 pathways. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 160 423–428. 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.09.053 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

