S100A8 and S100A9 Promote Apoptosis of Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia Cells
- PMID: 32903598
- PMCID: PMC7438788
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01258
S100A8 and S100A9 Promote Apoptosis of Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia Cells
Abstract
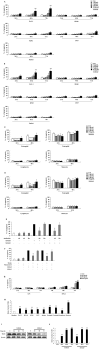
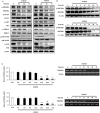
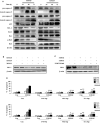
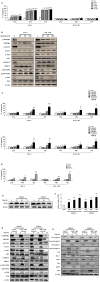
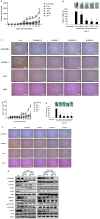
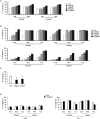
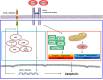
S100A8 and S100A9 function as essential factors in inflammation and also exert antitumor or tumorigenic activity depending on the type of cancer. Chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL) is a rare hematological malignancy having elevated levels of eosinophils and characterized by the presence of the FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion gene. In this study, we examined the pro-apoptotic mechanisms of S100A8 and S100A9 in FIP1L1-PDGFRα+ eosinophilic cells and hypereosinophilic patient cells. S100A8 and S100A9 induce apoptosis of the FIP1L1-PDGFRα+ EoL-1 cells via TLR4. The surface TLR4 expression increased after exposure to S100A8 and S100A9 although total TLR4 expression decreased. S100A8 and S100A9 suppressed the FIP1L1-PDGFRα-mediated signaling pathway by downregulating FIP1L1-PDGFRα mRNA and protein expression and triggered cell apoptosis by regulating caspase 9/3 pathway and Bcl family proteins. S100A8 and S100A9 also induced apoptosis of imatinib-resistant EoL-1 cells (EoL-1-IR). S100A8 and S100A9 blocked tumor progression of xenografted EoL-1 and EoL-1-IR cells in NOD-SCID mice and evoked apoptosis of eosinophils derived from hypereosinophilic syndrome as well as chronic eosinophilic leukemia. These findings may contribute to a progressive understanding of S100A8 and S100A9 in the pathogenic and therapeutic mechanism of hematological malignancy.
Keywords: FIP1L1-PDGFRα; S100 protein; TLR4; chronic eosinophilic leukemia; imatinib resistance.
Copyright © 2020 Lee, Lee, Kashif, Yang, Nam, Song, Gong, Hong, Kim, Seok, Lee, Sung and Kim.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

